Cost-effective therapeutic hypothermia treatment device for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
- PMID: 23319871
- PMCID: PMC3540914
- DOI: 10.2147/MDER.S39254
Cost-effective therapeutic hypothermia treatment device for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
Abstract
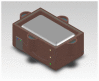
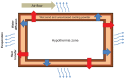
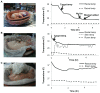
Despite recent advances in neonatal care and monitoring, asphyxia globally accounts for 23% of the 4 million annual deaths of newborns, and leads to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). Occurring in five of 1000 live-born infants globally and even more in developing countries, HIE is a serious problem that causes death in 25%-50% of affected neonates and neurological disability to at least 25% of survivors. In order to prevent the damage caused by HIE, our invention provides an effective whole-body cooling of the neonates by utilizing evaporation and an endothermic reaction. Our device is composed of basic electronics, clay pots, sand, and urea-based instant cold pack powder. A larger clay pot, lined with nearly 5 cm of sand, contains a smaller pot, where the neonate will be placed for therapeutic treatment. When the sand is mixed with instant cold pack urea powder and wetted with water, the device can extract heat from inside to outside and maintain the inner pot at 17°C for more than 24 hours with monitoring by LED lights and thermistors. Using a piglet model, we confirmed that our device fits the specific parameters of therapeutic hypothermia, lowering the body temperature to 33.5°C with a 1°C margin of error. After the therapeutic hypothermia treatment, warming is regulated by adjusting the amount of water added and the location of baby inside the device. Our invention uniquely limits the amount of electricity required to power and operate the device compared with current expensive and high-tech devices available in the United States. Our device costs a maximum of 40 dollars and is simple enough to be used in neonatal intensive care units in developing countries.
Keywords: birth asphyxia; evaporative cooling; hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy; neuroprotection; therapeutic hypothermia.
Figures



References
-
- Cooper DJ. Induced hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: pathophysiology, current treatment, and nursing considerations. Neonatal Netw. 2011;30(1):29–35. - PubMed
-
- Brann AW., Jr Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (asphyxia) Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986;33(3):451–464. - PubMed
-
- Merrill L. Therapeutic hypothermia to treat hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in newborns: implications for nurses. Nurs Womens Health. 2012;16(2):126–134. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

