Tuberculoma of the tongue presenting as hemimacroglossia
- PMID: 23319955
- PMCID: PMC3538444
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/548350
Tuberculoma of the tongue presenting as hemimacroglossia
Abstract
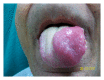
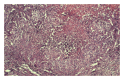
The underdiagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis lesions, along with an emerging global resistance to antitubercular drugs, warrants an increased awareness of the involvement of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in atypical lesions of oral cavity. Tongue is the most common site of oral tuberculosis. We report a rare presentation of lingual tuberculosis in a 65-year-old male, a chronic tobacco chewer, who came to us with swelling of the tongue which apparently looked like hemimacroglossia, leading to the clinical diagnosis of submucosal carcinoma of tongue. Enlargement of tongue is a slow process resulting from gradual invasion and lodging of bacilli in the tongue. Biopsy and histopathological examination revealed tuberculous etiology of the lesion and the patient responded well to antitubercular therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Yepes JF, Sullivan J, Pinto A. Tuberculosis: medical management update. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontology. 2004;98(3):267–273. - PubMed
-
- Al-Serhani AM. Mycobacterial infection of the head and neck: presentation and diagnosis. Laryngoscope. 2001;111(11):2012–2016. - PubMed
-
- Rafailidis PI, Avramopoulos I, Sapkas G, Falagas ME. Multidrug-resistant tuberculous spondylodiscitis: need for aggressive management and drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. Journal of Infection. 2006;52(2):e35–e37. - PubMed
-
- Iype EM, Ramdas K, Pandey M, et al. Primary tuberculosis of the tongue: report of three cases. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 2001;39(5):402–403. - PubMed
-
- Mohanapriya T, Singh KB, Arulappan T, Dhanasekar T. Lingual tuberculosis. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis. 2012;59(1):39–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources