Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune bullous dermatosis
- PMID: 23320017
- PMCID: PMC3540916
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/369546
Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune bullous dermatosis
Abstract
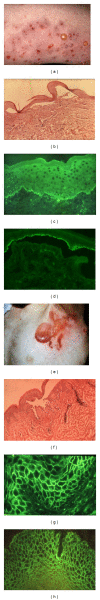
The authors present their experience related to the diagnosis, treatment, and followup of 431 patients with bullous pemphigoid, 14 patients with juvenile bullous pemphigoid, and 273 patients with pemphigus. The detection of autoantibodies plays an outstanding role in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Paraneoplastic pemphigoid is suggested to be a distinct entity from the group of bullous pemphigoid in view of the linear C3 deposits along the basement membrane of the perilesional skin and the "ladder" configuration of autoantibodies demonstrated by western blot analysis. It is proposed that IgA pemphigoid should be differentiated from the linear IgA dermatoses. Immunosuppressive therapy is recommended in which the maintenance dose of corticosteroid is administered every second day, thereby reducing the side effects of the corticosteroids. Following the detection of IgA antibodies (IgA pemphigoid, linear IgA bullous dermatosis, and IgA pemphigus), diamino diphenyl sulfone (dapsone) therapy is preferred alone or in combination. The clinical relevance of autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune bullous dermatosis is stressed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A child with antibodies targeting both linear IgA bullous dermatosis and bullous pemphigoid antigens.Arch Dermatol. 1995 Dec;131(12):1438-42. Arch Dermatol. 1995. PMID: 7492135
-
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis of childhood with autoantibodies to a 230 kDa epidermal antigen.Pediatr Dermatol. 1994 Jun;11(2):139-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1994.tb00568.x. Pediatr Dermatol. 1994. PMID: 8041654
-
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis. Characterization of a subset of patients with concurrent IgA and IgG anti-basement membrane autoantibodies.Arch Dermatol. 1995 Dec;131(12):1432-7. doi: 10.1001/archderm.131.12.1432. Arch Dermatol. 1995. PMID: 7492134
-
Subepithelial autoimmune bullous dermatoses disease activity assessment and therapy.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Jul;85(1):18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.161. Epub 2021 Mar 5. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33684494 Review.
-
Complement Activation in Autoimmune Bullous Dermatoses: A Comprehensive Review.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1477. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01477. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31293600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunologic overlap in a case of linear IgG/IgA bullous dermatosis responsive to rituximab.JAAD Case Rep. 2021 Jan 11;9:57-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.12.029. eCollection 2021 Mar. JAAD Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33665277 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comprehensive review on the pathophysiology, clinical variants and management of pemphigus (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Nov;22(5):1335. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10770. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34630689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Husz S, Heszler E, Török L. Paraneoplasmic bullosis. Dermatologica. 1970;141(6):421–427. - PubMed
-
- Jukić IL, Marinović B. Significance of immunofluorescence in the diagnosis of autoimmune bullous dermatoses. Clinics in Dermatology. 2011;29(4):389–397. - PubMed
-
- Gammon WR, Briggaman RA, Inman AO., III Differentiating anti-lamina lucida and anti-sublamina densa anti-BMZ antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence on 1.0 M sodium chloride-separated skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1984;82(2):139–144. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto T, Ogawa MM, Konohana A, Nishikawa T. Detection of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus antigens by immunoblot analysis using different antigen sources. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1990;94(3):327–331. - PubMed
-
- Kiss M, Husz S, Molnár K, Dobozy A. Identification of different circulating autoantibodies in patients with bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris by means of immunoblotting. Acta Microbiologica et Immunologica Hungarica. 1996;43(2-3):115–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

