Brazilian green propolis: anti-inflammatory property by an immunomodulatory activity
- PMID: 23320022
- PMCID: PMC3541042
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/157652
Brazilian green propolis: anti-inflammatory property by an immunomodulatory activity
Abstract
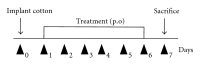
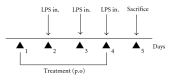
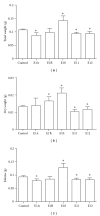
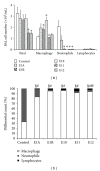
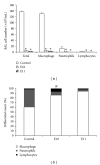
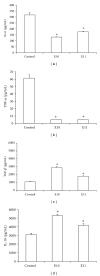
The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activities of green propolis extracts from Apis mellifera were investigated using acute and chronic inflammation models. Swiss mice were anesthetized and a cotton pellet granuloma was implanted in subcutaneous tissue. Then the mice were divided into six groups and received apyrogenic water or different propolis extracts by oral route (5 mg/kg). According to the treatment the groups were designated as E1A, E1B, E10, E11, and E12. The control group received apyrogenic water. The treatment was performed by six days when the mice were killed. The blood and the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) were collected to measure the leukocyte recruitment. In acute pulmonary inflammation, Balb/c mice received lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of Escherichia coli by intranasal route for three days. Concomitantly the mice received by oral route apyrogenic water (control) or E10 and E11 propolis extracts. BAL was performed to assess the inflammatory infiltrate and cytokine quantification. The results showed that the E11 extract has anti-inflammatory property in both models by the inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines and increase of anti-inflammatory cytokines suggesting an immunomodulatory activity.
Figures
References
-
- Marcucci MC, Rodriguez J, Ferreres F, Bankova V, Groto R, Popov S. Chemical composition of Brazilian propolis from Sao Paulo State. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung C. 1998;3(1-2):117–119.
-
- Park YK, Paredes-Guzman JF, Aguiar CL, Alencar SM, Fujiwara FY. Chemical constituents in Baccharis dracunculifolia as the main botanical origin of southeastern Brazilian propolis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2004;52(5):1100–1103. - PubMed
-
- de Barros MP, Sousa JPB, Bastos JK, de Andrade SF. Effect of Brazilian green propolis on experimental gastric ulcers in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2007;110(3):567–571. - PubMed
-
- Reis CMF, Carvalho JCT, Caputo LRG, et al. Atividade antiinflamatória, antiúlcera gástrica e toxicidade subcrônica do extrato etanólico de própolis. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia. 2000;10:43–49.
-
- Tavares DC, Barcelos GR, Silva LF, Chacon Tonin CC, Bastos JK. Propolis-induced genotoxicity and antigenotoxicity in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Toxicology in Vitro. 2006;20(7):1154–1158. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

