Study of the effects of monacolin k and other constituents of red yeast rice on obesity, insulin-resistance, hyperlipidemia, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using a mouse model of metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 23320041
- PMCID: PMC3541547
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/892697
Study of the effects of monacolin k and other constituents of red yeast rice on obesity, insulin-resistance, hyperlipidemia, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using a mouse model of metabolic syndrome
Abstract
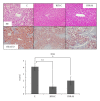
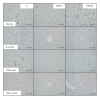
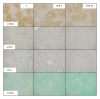
Purpose. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a progressive and intractable disease associated with metabolic syndrome. Red yeast rice (RYR) contains monacolin K, a potent inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, and its consumption decreases cholesterol and triglyceride levels. We examined the efficacy of RYR constituents using a novel metabolic syndrome-NAFLD mouse model (MSG mice). Methods. Two types of RYR grown under different culture conditions were used. 1P-DU contained only 0.002 g/100 g of monacolin K, whereas 3P-D1 contained 0.131 g/100 g. MSG mice were divided into three groups: control (C) group fed standard food, RYR-C group fed standard food with 1% 1P-DU, and RYR-M group fed standard food with 1% 3P-D1. Mice were examined from 12 to 24 weeks of age. Results. Serum insulin, leptin, and liver damage as well as macrophage aggregation in visceral fat in RYR-C and RYR-M groups were lower than those in C group. The serum adiponectin levels in RYR-C group were significantly higher than those in RYR-M and C groups. Conclusions. RYR was effective against obesity-related inflammation, insulin resistance, and NAFLD in MSG mice irrespective of monacolin K levels. GABA and various peptides produced during fermentation were determined as the active constituents of RYR.
Figures


References
-
- Williams CD, Stengel J, Asike MI, et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: a prospective study. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(1):124–131. - PubMed
-
- Farrell GC, Larter CZ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2006;43(2, supplement 1):S99–S112. - PubMed
-
- Musso G, Gambino R, Cassader M, Pagano G. A meta-analysis of randomized trials for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;52(1):79–104. - PubMed
-
- Gastaldelli A, Harrison SA, Belfort-Aguilar R, et al. Importance of changes in adipose tissue insulin resistance to histological response during thiazolidinedione treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2009;50(4):1087–1093. - PubMed
-
- Georgescu EF. Angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of NASH/NAFLD: could they be a first-class option? Advances in therapy. 2008;25(11):1141–1174. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

