Increases in [3H]muscimol and [3H]flumazenil binding in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia are linked to α4 and γ2S mRNA levels respectively
- PMID: 23320076
- PMCID: PMC3540049
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052724
Increases in [3H]muscimol and [3H]flumazenil binding in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia are linked to α4 and γ2S mRNA levels respectively
Abstract
Background: GABA(A) receptors (GABA(A)R) are composed of several subunits that determine sensitivity to drugs, synaptic localisation and function. Recent studies suggest that agonists targeting selective GABA(A)R subunits may have therapeutic value against the cognitive impairments observed in schizophrenia. In this study, we determined whether GABA(A)R binding deficits exist in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) of people with schizophrenia and tested if changes in GABA(A)R binding are related to the changes in subunit mRNAs. The GABA orthosteric and the benzodiazepine allosteric binding sites were assessed autoradiographically using [(3)H]Muscimol and [(3)H]Flumazenil, respectively, in a large cohort of individuals with schizophrenia (n = 37) and their matched controls (n = 37). We measured, using qPCR, mRNA of β (β1, β2, β3), γ (γ1, γ2, γ2S for short and γ2L for long isoform, γ3) and δ subunits and used our previous measurements of GABA(A)R α subunit mRNAs in order to relate mRNAs and binding through correlation and regression analysis.
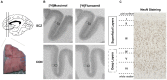
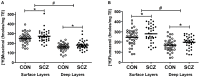
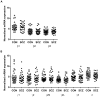
Results: Significant increases in both [(3)H]Muscimol (p = 0.016) and [(3)H]Flumazenil (p = 0.012) binding were found in the DLPFC of schizophrenia patients. Expression levels of mRNA subunits measured did not show any significant difference in schizophrenia compared to controls. Regression analysis revealed that in schizophrenia, the [(3)H]Muscimol binding variance was most related to α4 mRNA levels and the [(3)H]Flumazenil binding variance was most related to γ2S subunit mRNA levels. [(3)H]Muscimol and [(3)H]Flumazenil binding were not affected by the lifetime anti-psychotics dose (chlorpromazine equivalent).
Conclusions: We report parallel increases in orthosteric and allosteric GABA(A)R binding sites in the DLPFC in schizophrenia that may be related to a "shift" in subunit composition towards α4 and γ2S respectively, which may compromise normal GABAergic modulation and function. Our results may have implications for the development of treatment strategies that target specific GABA(A)R receptor subunits.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Changes in hippocampal GABAA receptor subunit composition in bipolar 1 disorder.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005 Aug 18;138(2):145-55. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.04.005. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15950312
-
Alterations in GABA-related transcriptome in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia.Mol Psychiatry. 2008 Feb;13(2):147-61. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002011. Epub 2007 May 1. Mol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17471287 Free PMC article.
-
Acute pentylenetetrazol injection reduces rat GABAA receptor mRNA levels and GABA stimulation of benzodiazepine binding with No effect on benzodiazepine binding site density.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Jun;289(3):1626-33. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10336561
-
Cell and receptor type-specific alterations in markers of GABA neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia.Neurotox Res. 2008 Oct;14(2-3):237-48. doi: 10.1007/BF03033813. Neurotox Res. 2008. PMID: 19073429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABA(A) receptors and their associated proteins: implications in the etiology and treatment of schizophrenia and related disorders.Neuropharmacology. 2009 Oct-Nov;57(5-6):481-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.07.027. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19631671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Region-specific and dose-specific effects of chronic haloperidol exposure on [3H]-flumazenil and [3H]-Ro15-4513 GABAA receptor binding sites in the rat brain.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 Dec;41:106-117. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2020.10.004. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33153853 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimaging studies of GABA in schizophrenia: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 6;7(6):e1147. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.124. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28585933 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of LINE-1 Elements in DNA from Postmortem Brains of Individuals with Schizophrenia.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 Dec;42(13):2602-2611. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.115. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28585566 Free PMC article.
-
The Endocannabinoid System across Postnatal Development in Transmembrane Domain Neuregulin 1 Mutant Mice.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 7;9:11. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00011. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29467679 Free PMC article.
-
Markers of inflammation and stress distinguish subsets of individuals with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Transl Psychiatry. 2014 Feb 25;4(2):e365. doi: 10.1038/tp.2014.8. Transl Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24569695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daskalakis ZJ, Fitzgerald PB, Christensen BK (2007) The role of cortical inhibition in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. Brain Research Reviews 56: 427–442. - PubMed
-
- Connolly CN, Uren JM, Thomas P, Gorrie GH, Gibson A, et al. (1999) Subcellular localization and endocytosis of homomeric gamma2 subunit splice variants of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences 13: 259–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

