Neurogenic and neurotrophic effects of BDNF peptides in mouse hippocampal primary neuronal cell cultures
- PMID: 23320097
- PMCID: PMC3539976
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053596
Neurogenic and neurotrophic effects of BDNF peptides in mouse hippocampal primary neuronal cell cultures
Abstract
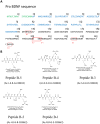
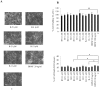
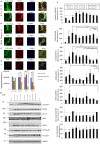
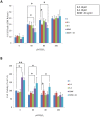
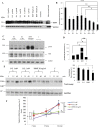
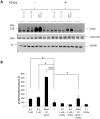
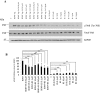
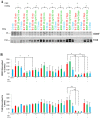
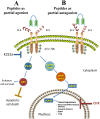
The level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a member of the neurotrophin family, is down regulated in Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), depression, stress, and anxiety; conversely the level of this neurotrophin is increased in autism spectrum disorders. Thus, modulating the level of BDNF can be a potential therapeutic approach for nervous system pathologies. In the present study, we designed five different tetra peptides (peptides B-1 to B-5) corresponding to different active regions of BDNF. These tetra peptides were found to be non-toxic, and they induced the expression of neuronal markers in mouse embryonic day 18 (E18) primary hippocampal neuronal cultures. Additionally, peptide B-5 induced the expression of BDNF and its receptor, TrkB, suggesting a positive feedback mechanism. The BDNF peptides induced only a moderate activation (phosphorylation at Tyr 706) of the TrkB receptor, which could be blocked by the Trk's inhibitor, K252a. Peptide B-3, when combined with BDNF, potentiated the survival effect of this neurotrophin on H(2)O(2)-treated E18 hippocampal cells. Peptides B-3 and B-5 were found to work as partial agonists and as partial antagonists competing with BDNF to activate the TrkB receptor in a dose-dependent manner. Taken together, these results suggest that the described BDNF tetra peptides are neurotrophic, can modulate BDNF signaling in a partial agonist/antagonist way, and offer a novel therapeutic approach to neural pathologies where BDNF levels are dysregulated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kaplan DR, Miller FD (2000) Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10: 381–391. - PubMed
-
- Chao MV (2003) Neurotrophins and their receptors: a convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat Rev Neurosci 4: 299–309. - PubMed
-
- Counts SE, Mufson EJ (2005) The role of nerve growth factor receptors in cholinergic basal forebrain degeneration in prodromal Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64: 263–272. - PubMed
-
- Tapia-Arancibia L, Aliaga E, Silhol M, Arancibia S (2008) New insights into brain BDNF function in normal aging and Alzheimer disease. Brain Res Rev 59: 201–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

