Oxidative stress contributes to endothelial dysfunction in mouse models of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
- PMID: 23320130
- PMCID: PMC3540964
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/686972
Oxidative stress contributes to endothelial dysfunction in mouse models of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
Abstract
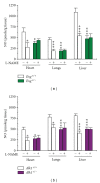
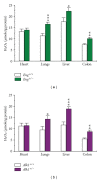
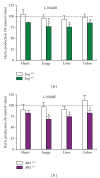
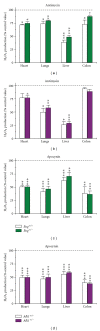
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is a vascular dysplasia caused by mutations in endoglin (ENG; HHT1) or activin receptor-like kinase (ALK1; HHT2) genes, coding for transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily receptors. We demonstrated previously that endoglin and ALK1 interact with endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) and affect its activation. Endothelial cells deficient in endoglin or ALK1 proteins show eNOS uncoupling, reduced NO, and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. In this study, we measured NO and H(2)O(2) levels in several organs of adult Eng and Alk1 heterozygous mice, to ascertain whether decreased NO and increased ROS production is a generalized manifestation of HHT. A significant reduction in NO and increase in ROS production were found in several organs, known to be affected in patients. ROS overproduction in mutant mice was attributed to eNOS, as it was L-NAME inhibitable. Mitochondrial ROS contribution, blocked by antimycin, was highest in liver while NADPH oxidase, inhibited by apocynin, was a major source of ROS in the other tissues. However, there was no difference in antimycin- and apocynin-inhibitable ROS production between mutant and control mice. Our results indicate that eNOS-derived ROS contributes to endothelial dysfunction and likely predisposes to disease manifestations in several organs of HHT patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoglin and activin receptor-like kinase 1 heterozygous mice have a distinct pulmonary and hepatic angiogenic profile and response to anti-VEGF treatment.Angiogenesis. 2014 Jan;17(1):129-46. doi: 10.1007/s10456-013-9383-4. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Angiogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24061911
-
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, a vascular dysplasia affecting the TGF-beta signaling pathway.Clin Med Res. 2006 Mar;4(1):66-78. doi: 10.3121/cmr.4.1.66. Clin Med Res. 2006. PMID: 16595794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spontaneous adult-onset pulmonary arterial hypertension attributable to increased endothelial oxidative stress in a murine model of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Mar;30(3):509-17. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.200121. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20042709
-
Contribution of oxidative stress to endothelial dysfunction in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Front Genet. 2015 Feb 13;6:34. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00034. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25763011 Free PMC article.
-
Endoglin and alk1 as therapeutic targets for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Oct;21(10):933-947. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1365839. Epub 2017 Aug 20. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28796572 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Second-Hits in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 5;9(11):3571. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113571. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33167572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress-induced MMP- and γ-secretase-dependent VE-cadherin processing is modulated by the proteasome and BMP9/10.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 11;13(1):597. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-27308-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36631513 Free PMC article.
-
Acarbose Accelerates Wound Healing via Akt/eNOS Signaling in db/db Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7809581. doi: 10.1155/2017/7809581. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28373902 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired wound repair in adult endoglin heterozygous mice associated with lower NO bioavailability.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Jan;134(1):247-255. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.263. Epub 2013 Jun 13. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 23765132
-
Syk promotes phagocytosis by inducing reactive oxygen species generation and suppressing SOCS1 in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022 Jan-Dec;36:3946320221133018. doi: 10.1177/03946320221133018. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36214175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McDonald J, Bayrak-Toydemir P, Pyeritz RE. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: an overview of diagnosis, management, and pathogenesis. Genetics in Medicine. 2011;13(7):607–616. - PubMed
-
- Barbara NP, Wrana JL, Letarte M. Endoglin is an accessory protein that interacts with the signaling receptor complex of multiple members of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1999;274(2):584–594. - PubMed
-
- David L, Mallet C, Mazerbourg S, Feige JJ, Bailly S. Identification of BMP9 and BMP10 as functional activators of the orphan activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) in endothelial cells. Blood. 2007;109(5):1953–1961. - PubMed
-
- Gallione CJ, Repetto GM, Legius E, et al. A combined syndrome of juvenile polyposis and hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia associated with mutations in MADH4 (SMAD4) The Lancet. 2004;363(9412):852–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

