Levels of interferon-gamma increase after treatment for latent tuberculosis infection in a high-transmission setting
- PMID: 23320165
- PMCID: PMC3539439
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/757152
Levels of interferon-gamma increase after treatment for latent tuberculosis infection in a high-transmission setting
Abstract
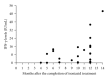
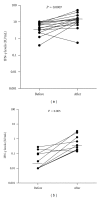
Objectives. We investigated IFN-γ levels before and after a six month course of isoniazid among individuals with latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) in a high-transmission setting. Design. A total of 26 household contacts of pulmonary tuberculosis patients who were positive for LTBI by tuberculin skin test completed six months of treatment and submitted a blood sample for a follow-up examination. The IFN-γ response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigens was measured, and the results before and after the completion of LTBI treatment were compared. Results. Of the 26 study participants, 25 (96%) showed an IFN-γ level higher than their baseline level before treatment (P ≤ 0.001). Only one individual had a decreased IFN-γ level after treatment but remained positive for LTBI. Conclusion. In a high-transmission setting, the IFN-γ level has increased after LTBI treatment. Further studies must be undertaken to understand if this elevation is transient.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen P, Munk ME, Pollock JM, Doherty TM. Specific immune-based diagnosis of tuberculosis. The Lancet. 2000;356(9235):1099–1104. - PubMed
-
- Pai M, Riley LW, Colford JM. Interferon-γ assays in the immunodiagnosis of tuberculosis: a systematic review. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2004;4(12):761–766. - PubMed
-
- Eum SY, Lee YJ, Kwak HK, et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic utility of a whole-blood interferon-γ assay for determining the risk of exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG)-vaccinated individuals. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease. 2008;61(2):181–186. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

