Patient attitudes to tonsillectomy
- PMID: 23320167
- PMCID: PMC3540685
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/735684
Patient attitudes to tonsillectomy
Abstract
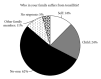
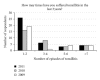
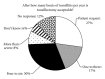
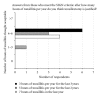
Introduction. Recent changes to primary care trusts' Procedures of Limited Clinical Value (PLCV) policy mean that otolaryngologists must now follow policy rather than exercising clinical judgment when listing patients for tonsillectomy. Objectives. To gauge perception within the general public of when tonsillectomy is acceptable and to compare this to the current policy. Method. All patients or their parents attending the adult and paediatric outpatient ENT departments were asked to anonymously complete questionnaires. Results. One hundred and twenty-five completed questionnaires were collected. Thirty-one percent of respondents thought tonsillectomy should be offered solely on patient request, 19% after one to three bouts, and 35% after four to six bouts of tonsillitis. Only 9% thought the current guidelines were reasonable. Patients who had suffered recurrent tonsillitis or had undergone previous tonsillectomy generally thought tonsillectomy advisable after more bouts of tonsillitis than those who had not. Fourteen patients fulfilled the SIGN guidelines for tonsillectomy for recurrent tonsillitis. Of these, 13 (93%) felt that suffering 4-6 bouts of tonsillitis was reasonable before tonsillectomy. Conclusion. All patients we surveyed who meet the current PLCV and SIGN guidelines regarding the appropriateness of tonsillectomy for recurrent tonsillitis perceive that they are excessive, believing that 4-6 bouts of recurrent tonsillitis are adequate to justify tonsillectomy.
References
-
- Derby County Primary Care Trust. Derby County Commissioning policy for procedures of limited clinical value. April 2010, http://www.derbycitypct.nhs.uk/
-
- Royal College of Surgeons of England. Procedures of limited clinical value—Royal College of Surgeons briefing. January 2011, http://www.rcseng.ac.uk/
-
- Department of Health. Equity and excellence: liberating the NHS-White Paper executive summary. August 2010, http://www.dh.gov.uk/
-
- Banks MH, Beresford SAA, Morrell DC, Waller JJ, Watkins CJ. Factors influencing demand for primary medical care in women aged 20–44 years: a preliminary report. International Journal of Epidemiology. 1975;4(3):189–195. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous