Recurrent dislocation of the patella in kabuki make-up syndrome
- PMID: 23320229
- PMCID: PMC3535732
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/501453
Recurrent dislocation of the patella in kabuki make-up syndrome
Abstract
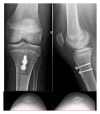
Two patients with Kabuki make-up syndrome with bilateral recurrent dislocation of the patella are presented. They had generalized ligamentous laxity and patellofemoral dysplasia. Both developed patellar dislocation in adolescence and required surgery, with medial transfer of the tibial tuberosity associated with vastus medialis plasty (Insall technique). One postoperative complication occurred in one case: a nondisplaced tibia fracture at the sixth postoperative week that healed with conservative means. Final results were good in both cases. Good surgical results can be achieved in patellar dislocation in patients with Kabuki syndrome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Incidence and radiologic predictor of postoperative patellar instability after Fulkerson procedure of the tibial tuberosity for recurrent patellar dislocation.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012 Oct;20(10):2062-70. doi: 10.1007/s00167-011-1832-2. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012. PMID: 22203044 Clinical Trial.
-
A pre-operative grade 3 J-sign adversely affects short-term clinical outcome and is more likely to yield MPFL residual graft laxity in recurrent patellar dislocation.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020 Jul;28(7):2147-2156. doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05736-4. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020. PMID: 31612265
-
Recurrent dislocation of the patella in Kabuki make-up syndrome.J Pediatr Orthop. 1993 Mar-Apr;13(2):265-7. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993. PMID: 8459025
-
[Interim results of surgical therapy of patellar dislocation by Insall proximal reconstruction].Unfallchirurg. 1998 Jun;101(6):446-53. doi: 10.1007/s001130050294. Unfallchirurg. 1998. PMID: 9677843 Review. German.
-
Traumatic patellar dislocation in children and adolescents: treatment update and literature review.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2004 Feb;16(1):29-36. doi: 10.1097/00008480-200402000-00007. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2004. PMID: 14758111 Review.
Cited by
-
Patellar Dislocation in a Patient with Kabuki Syndrome with Severe Mental Retardation: A Case Report.Prog Rehabil Med. 2019 Jun 12;4:20190012. doi: 10.2490/prm.20190012. eCollection 2019. Prog Rehabil Med. 2019. PMID: 32789259 Free PMC article.
-
Patellar Instability in the Skeletally Immature.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018 Jun;11(2):172-181. doi: 10.1007/s12178-018-9472-5. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018. PMID: 29682681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adam MP, Hudgins L. Kabuki syndrome: a review. Clinical Genetics. 2005;67(3):209–219. - PubMed
-
- Kawame H, Hannibal MC, Hudgins L, Pagon RA. Phenotypic spectrum and management issues in Kabuki syndrome. Journal of Pediatrics. 1999;134(4):480–485. - PubMed
-
- Kuroki Y, Suzuki Y, Chyo H, et al. A new malformation syndrome of long palpebral fissures, large ears, depressed nasal tip, and skeletal anomalies associated with postnatal dwarfism and mental retardation. Journal of Pediatrics. 1981;99(4):570–573. - PubMed
-
- Niikawa N, Kuroki Y, Kajii T, et al. Kabuki make-up (Niikawa-Kuroki) syndrome: a study of 62 patients. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 1988;31(3):565–589. - PubMed
-
- Niikawa N, Matsuura N, Fukushima Y. Kabuki make up syndrome: a syndrome of mental retardation, unusual facies, large and protruding ears, and postnatal growth deficiency. Journal of Pediatrics. 1981;99(4):565–569. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

