Lipoprotein lipase links vitamin D, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional epidemiological study
- PMID: 23320821
- PMCID: PMC3570389
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-17
Lipoprotein lipase links vitamin D, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional epidemiological study
Abstract
Background: Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] play important roles in the regulation of lipid metabolism. Although dyslipidemia is associated with insulin resistance (IR) and type 2 diabetes (T2D), there are limited data available regarding the relationship of LPL and 25(OH)D to IR and T2D at a population level. The objective of the present study is to investigate the associations of LPL and 25(OH)D with IR and T2D in a Chinese population.
Methods: The study cohort consisted of 2708 subjects (1326 males, 1382 females; mean age 48.5 ± 12.6 years) in main communities of Harbin, China. Serum 25(OH)D, LPL, free fatty acids (FFAs), fasting glucose (FG), fasting insulin, lipid profile, apoA and apoB concentrations were measured.
Results: Serum 25(OH)D concentration was positively associated with LPL (β = 0.168, P < 0.001). LPL was inversely associated with IR and T2D. Subjects in the lowest quartile of LPL had the highest risk of IR [odds ratio (OR) = 1.85, 95% CI = 1.22-2.68] and T2D (OR = 1.65, 95% CI = 1.14-2.38). Serum 25(OH)D was also inversely associated with IR and T2D. Vitamin D deficiency [25(OH)D < 20 ng/ml] was associated with an increasing risk of IR (OR = 1.91, 95% CI = 1.23-2.76) and T2D (OR = 2.06, 95% CI = 1.37-3.24). The associations of 25(OH)D with IR and T2D were attenuated by further adjustment for LPL.
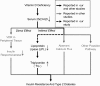
Conclusions: LPL is associated with serum 25(OH)D, IR and T2D in the Chinese population. These results suggest a potential mediating role of LPL in the associations of 25(OH)D with IR and T2D.
Figures
References
-
- Hide WA, Chan L, Li WH. Structure and evolution of the lipase superfamily. Journal of lipid research. 1992;33(2):167–178. - PubMed
-
- Mead JR, Irvine SA, Ramji DP. Lipoprotein lipase: structure, function, regulation, and role in disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 2002;80(12):753–769. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg IJ, Merkel M. Lipoprotein lipase: physiology, biochemistry, and molecular biology. Frontiers in bioscience: a journal and virtual library. 2001;6:D388–D405. - PubMed
-
- Hanyu O, Miida T, Kosuge K, Ito T, Soda S, Hirayama S, Wardaningsih E, Fueki Y, Obayashi K, Aizawa Y. Preheparin lipoprotein lipase mass is a practical marker of insulin resistance in ambulatory type 2 diabetic patients treated with oral hypoglycemic agents. Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry. 2007;384(1-2):118–123. - PubMed
-
- Eckel RH, Yost TJ, Jensen DR. Alterations in lipoprotein lipase in insulin resistance. International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders: journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity. 1995;19(Suppl 1):S16–S21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

