MEK inhibition induced downregulation of MRP1 and MRP3 expression in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 23320839
- PMCID: PMC3558388
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-3
MEK inhibition induced downregulation of MRP1 and MRP3 expression in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) exhibits strong intrinsic and acquired drug resistance which is the main obstacle to chemotherapy. Overexpression of ATP binding cassette (ABC) proteins correlates with activation of mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in HCC. Here, we systematically investigated the inhibition of MAPK pathway and its role in regulating HCC cell growth as well as ABC proteins MRP1 and MRP3 expression.
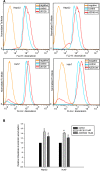
Methods: The Raf1 kinase inhibitor (GW5074) and different MEK inhibitors (U0126 and AZD6244) were used to treat HCC cells to identify their effects on HCC cell growth and ABC proteins expression in vitro. Cell viability tests were performed after the treatment of MAPK pathway inhibitors and in combination with gemcitabine or doxorubicin. Western blot was applied to assess the changes of MAPK pathway and protein expression of MRP1 and MRP3. Flow cytometry was used to measure intracellular doxorubicin accumulation after the treatment of MEK inhibitors.
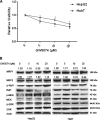
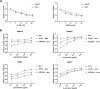
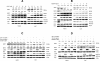
Results: Both Raf1 inhibitor (GW5074) and MEK inhibitors (U0126 and AZD6244) suppressed HCC cell growth in a dose dependent manner. Pre-treatment of MEK inhibitor U0126 or AZD6244 sensitized HCC cells to gemcitabine or doxorubicin based chemotherapy. Raf1 inhibitor GW5074 had no effect on MRP1 and MRP3 protein expression. Treatment of gemcitabine or doxorubicin activated phosphorylated ERK and induced the upregulation of MRP1 and MRP3. MEK inhibitors U0126 and AZD6244 deactivated phosphorylated ERK, decreased endogenous MRP1 expression, reversed gemcitabine or doxorubicin induced MRP1 and MRP3 upregulation, and increased the intracellular doxorubicin accumulation.
Conclusion: This study provides evidence that MEK inhibitors sensitize HCC cells to chemotherapy by increasing intracellular chemodrug accumulation. MEK inhibirors U0126 and AZD6244 reduced MRP1 as well as MRP3 expression, and may contribute partially to the sensitization. The combination of MEK inhibitor and conventional chemotherapy may offer new therapeutic option for the treatment of resistant HCC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reversal of multidrug resistance by gefitinib via RAF1/ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer cell line.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012 Dec;295(12):2122-8. doi: 10.1002/ar.22552. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22907845
-
MEK inhibitor enhances sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs in multidrug resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Oncol Lett. 2017 Sep;14(3):3089-3095. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6494. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28928846 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of doxorubicin on MEK-ERK signaling predicts its efficacy in HCC.J Surg Res. 2008 Dec;150(2):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2008.01.029. Epub 2008 Mar 3. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 18468633
-
Blocking MAPK/ERK pathway sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to temozolomide via downregulating MGMT expression.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Oct;8(20):1305. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5478. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33209885 Free PMC article.
-
U0126: Not only a MAPK kinase inhibitor.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 25;13:927083. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.927083. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine A3 receptor elicits chemoresistance mediated by multiple resistance-associated protein-1 in human glioblastoma stem-like cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 11;7(41):67373-67386. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12033. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27634913 Free PMC article.
-
Midkine as a potential diagnostic marker in epithelial ovarian cancer for cisplatin/paclitaxel combination clinical therapy.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 15;5(2):629-38. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25973302 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: efficacy and mode of action.Oncol Rev. 2014 May 28;8(1):246. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2014.246. eCollection 2014 Mar 17. Oncol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25992234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of neo-adjuvant Sorafenib treatment on liver transplantation in HCC patients - a prospective, randomized, double-blind, phase III trial.BMC Cancer. 2015 May 11;15:392. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1373-z. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25957784 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Upregulation of Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 1 by Allyl Isothiocyanate in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell: Involvement of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:903782. doi: 10.1155/2015/903782. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26273426 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

