Regulation of μ-opioid receptors: desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance
- PMID: 23321159
- PMCID: PMC3565916
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.112.005942
Regulation of μ-opioid receptors: desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance
Abstract
Morphine and related µ-opioid receptor (MOR) agonists remain among the most effective drugs known for acute relief of severe pain. A major problem in treating painful conditions is that tolerance limits the long-term utility of opioid agonists. Considerable effort has been expended on developing an understanding of the molecular and cellular processes that underlie acute MOR signaling, short-term receptor regulation, and the progression of events that lead to tolerance for different MOR agonists. Although great progress has been made in the past decade, many points of contention and controversy cloud the realization of this progress. This review attempts to clarify some confusion by clearly defining terms, such as desensitization and tolerance, and addressing optimal pharmacological analyses for discerning relative importance of these cellular mechanisms. Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating MOR function by phosphorylation relative to receptor desensitization and endocytosis are comprehensively reviewed, with an emphasis on agonist-biased regulation and areas where knowledge is lacking or controversial. The implications of these mechanisms for understanding the substantial contribution of MOR signaling to opioid tolerance are then considered in detail. While some functional MOR regulatory mechanisms contributing to tolerance are clearly understood, there are large gaps in understanding the molecular processes responsible for loss of MOR function after chronic exposure to opioids. Further elucidation of the cellular mechanisms that are regulated by opioids will be necessary for the successful development of MOR-based approaches to new pain therapeutics that limit the development of tolerance.
Figures


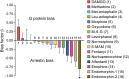
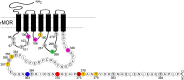
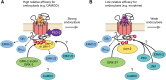
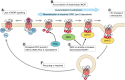
References
-
- Agnati LF, Ferré S, Lluis C, Franco R, Fuxe K. (2003) Molecular mechanisms and therapeutical implications of intramembrane receptor/receptor interactions among heptahelical receptors with examples from the striatopallidal GABA neurons. Pharmacol Rev 55:509–550 - PubMed
-
- Ammon-Treiber S, Höllt V. (2005) Morphine-induced changes of gene expression in the brain. Addict Biol 10:81–89 - PubMed
-
- Arttamangkul S, Alvarez-Maubecin V, Thomas G, Williams JT, Grandy DK. (2000) Binding and internalization of fluorescent opioid peptide conjugates in living cells. Mol Pharmacol 58:1570–1580 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 DA010154/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA010711/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA005010/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA012864/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J013269/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DA020836/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA027625/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA01863/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012864/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA020836/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA020570/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA027625/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA005010/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K0-5DA20570/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

