PAK-PIX interactions regulate adhesion dynamics and membrane protrusion to control neurite outgrowth
- PMID: 23321640
- PMCID: PMC3635460
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.112607
PAK-PIX interactions regulate adhesion dynamics and membrane protrusion to control neurite outgrowth
Abstract
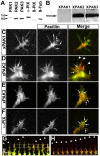
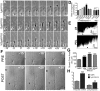
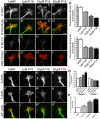
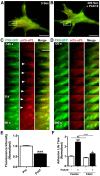
The roles of P21-activated kinase (PAK) in the regulation of axon outgrowth downstream of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins are poorly understood. Here we show that PAK1-3 and PIX are expressed in the developing spinal cord and differentially localize to point contacts and filopodial tips within motile growth cones. Using a specific interfering peptide called PAK18, we found that axon outgrowth is robustly stimulated on laminin by partial inhibition of PAK-PIX interactions and PAK function, whereas complete inhibition of PAK function stalls axon outgrowth. Furthermore, modest inhibition of PAK-PIX stimulates the assembly and turnover of growth cone point contacts, whereas strong inhibition over-stabilizes adhesions. Point mutations within PAK confirm the importance of PIX binding. Together our data suggest that regulation of PAK-PIX interactions in growth cones controls neurite outgrowth by influencing the activity of several important mediators of actin filament polymerization and retrograde flow, as well as integrin-dependent adhesion to laminin.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Paxillin-dependent paxillin kinase linker and p21-activated kinase localization to focal adhesions involves a multistep activation pathway.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 May;13(5):1550-65. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-02-0015. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12006652 Free PMC article.
-
PAK is regulated by PI3K, PIX, CDC42, and PP2Calpha and mediates focal adhesion turnover in the hyperosmotic stress-induced p38 pathway.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 5;283(36):24949-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801728200. Epub 2008 Jun 27. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18586681 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive p21-activated kinase (PAK) activation in breast cancer cells as a result of mislocalization of PAK to focal adhesions.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jun;15(6):2965-77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-08-0604. Epub 2004 Mar 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15047871 Free PMC article.
-
p85 beta-PIX is required for cell motility through phosphorylations of focal adhesion kinase and p38 MAP kinase.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Jul 15;307(2):315-28. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.03.028. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15893751
-
Pak to the future.Trends Cell Biol. 1999 Sep;9(9):350-5. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(99)01618-9. Trends Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10461188 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of ECM degradation and axon guidance by growth cone invadosomes.Development. 2015 Feb 1;142(3):486-96. doi: 10.1242/dev.108266. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Development. 2015. PMID: 25564649 Free PMC article.
-
Live Imaging of Cytoskeletal Dynamics in Embryonic Xenopus laevis Growth Cones and Neural Crest Cells.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2021 Apr 1;2021(4):pdb.prot104463. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot104463. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33272974 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperactivity of Rac1-GTPase pathway impairs neuritogenesis of cortical neurons by altering actin dynamics.Sci Rep. 2018 May 8;8(1):7254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25354-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29740022 Free PMC article.
-
Prenylated quinolinecarboxylic acid compound-18 prevents sensory nerve fiber outgrowth through inhibition of the interleukin-31 pathway.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 4;16(2):e0246630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246630. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33539470 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular basis of p21-activated kinase-associated neurodevelopmental disorders: From genotype to phenotype.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 2;17:1123784. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1123784. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36937657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

