Inhibition of N-terminal ATPase on HSP90 attenuates colitis through enhanced Treg function
- PMID: 23321985
- PMCID: PMC3748235
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2012.134
Inhibition of N-terminal ATPase on HSP90 attenuates colitis through enhanced Treg function
Abstract
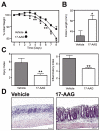
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory condition thought to reflect a failure of the enteral immune system to adequately regulate itself. Inflammatory stress drives upregulation of heat-shock proteins (HSPs), including the pro-inflammatory chaperone, HSP90. This protein sequesters the transcription factor, heat-shock factor 1 (HSF1) in the cytoplasm preventing transcription of a number of anti-inflammatory proteins. We hypothesized that inhibition of HSP90 would exert an anti-inflammatory effect and thereby attenuate intestinal inflammation in murine models of IBD. Inhibition of HSP90 with 17-allylaminogeldanamycin (17-AAG) reduced inflammation in acute dextran sodium sulfate and chronic CD45RB(High) colitis models coinciding with increased interleukin (IL)-10 production in the colon. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) from mice treated with 17-AAG demonstrated significantly greater suppressive capacity in vitro abolished in HSF1-/- or IL-10-/- cells. Finally, Tregs treated with 17-AAG exhibited increased nuclear localization of HSF1 with resultant upregulation of HSF1 response genes, including HSP70, HSP90 and IL-10.
Figures







References
-
- Singh B, et al. Control of intestinal inflammation by regulatory T cells. Immunol Rev. 2001;182:190–200. - PubMed
-
- Mottet C, Uhlig HH, Powrie F. Cutting edge: cure of colitis by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2003;170:3939–3943. - PubMed
-
- De AK, Kodys KM, Yeh BS, Miller-Graziano C. Exaggerated human monocyte IL-10 concomitant to minimal TNF-alpha induction by heat-shock protein 27 (Hsp27) suggests Hsp27 is primarily an antiinflammatory stimulus. J Immunol. 2000;165:3951–3958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

