Parallel photonic information processing at gigabyte per second data rates using transient states
- PMID: 23322052
- PMCID: PMC3562454
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2368
Parallel photonic information processing at gigabyte per second data rates using transient states
Abstract
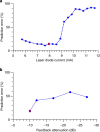
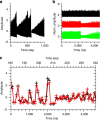
The increasing demands on information processing require novel computational concepts and true parallelism. Nevertheless, hardware realizations of unconventional computing approaches never exceeded a marginal existence. While the application of optics in super-computing receives reawakened interest, new concepts, partly neuro-inspired, are being considered and developed. Here we experimentally demonstrate the potential of a simple photonic architecture to process information at unprecedented data rates, implementing a learning-based approach. A semiconductor laser subject to delayed self-feedback and optical data injection is employed to solve computationally hard tasks. We demonstrate simultaneous spoken digit and speaker recognition and chaotic time-series prediction at data rates beyond 1 Gbyte/s. We identify all digits with very low classification errors and perform chaotic time-series prediction with 10% error. Our approach bridges the areas of photonic information processing, cognitive and information science.
Figures
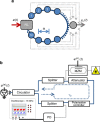


 , creating the laser input.
, creating the laser input.References
-
- Crutchfield J. P., William L. D. & Sudeshna S.. Introduction to focus issue: intrinsic and designed computation: information processing in dynamical systems—beyond the digital hegemony. Chaos 20, 037101–037107 (2010) . - PubMed
-
- Woods D. & Naughton T. J.. Optical computing: photonic neural networks. Nat. Phys. 8, 257–259 (2012) .
-
- Caulfield H. J. & Dolev S.. Why future supercomputing requires optics. Nat. Photon. 4, 261–263 (2010) .
-
- Jaeger H. & Haas H.. Harnessing nonlinearity: predicting chaotic systems and saving energy in wireless communication. Science 304, 78–80 (2004) . - PubMed
-
- Modha D. S. et al. Cognitive computing. Commun. ACM 54, 62–71 (2011) .
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

