Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation with the detoxified ligand monophosphoryl lipid A improves Alzheimer's disease-related pathology
- PMID: 23322736
- PMCID: PMC3562771
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1215165110
Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation with the detoxified ligand monophosphoryl lipid A improves Alzheimer's disease-related pathology
Abstract
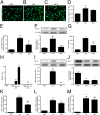
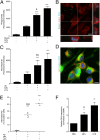
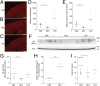
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia worldwide. The pathogenesis of this neurodegenerative disease, currently without curative treatment, is associated with the accumulation of amyloid β (Aβ) in brain parenchyma and cerebral vasculature. AD patients are unable to clear this toxic peptide, leading to Aβ accumulation in their brains and, presumably, the pathology associated with this devastating disease. Compounds that stimulate the immune system to clear Aβ may therefore have great therapeutic potential in AD patients. Monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) is an LPS-derived Toll-like receptor 4 agonist that exhibits unique immunomodulatory properties at doses that are nonpyrogenic. We show here that repeated systemic injections of MPL, but not LPS, significantly improved AD-related pathology in APP(swe)/PS1 mice. MPL treatment led to a significant reduction in Aβ load in the brain of these mice, as well as enhanced cognitive function. MPL induced a potent phagocytic response by microglia while triggering a moderate inflammatory reaction. Our data suggest that the Toll-like receptor 4 agonist MPL may be a treatment for AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.H., P.T.-J., A.-M.L., R.J., C.C., V.B., R.P., A.P., and D.L. are employees of GlaxoSmithKline Vaccines. This research was supported in part by GlaxoSmithKline Vaccines.
Figures



Comment in
-
Alzheimer disease: modified Salmonella toxin combats Alzheimer disease in mouse model.Nat Rev Neurol. 2013 Mar;9(3):120. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.15. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23399645 No abstract available.
-
A Toll road to Alzheimer disease?CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Jun;12(4):445-6. doi: 10.2174/18715273113129990067. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23746134 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

