Molecular pathways: current role and future directions of the retinoic acid pathway in cancer prevention and treatment
- PMID: 23322901
- PMCID: PMC3618522
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3175
Molecular pathways: current role and future directions of the retinoic acid pathway in cancer prevention and treatment
Abstract
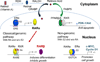
Retinoids and their naturally metabolized and synthetic products (e.g., all-trans retinoic acid, 13-cis retinoic acid, bexarotene) induce differentiation in various cell types. Retinoids exert their actions mainly through binding to the nuclear retinoic acid receptors (α, β, γ), which are transcriptional and homeostatic regulators with functions that are often compromised early in neoplastic transformation. The retinoids have been investigated extensively for their use in cancer prevention and treatment. Success has been achieved with their use in the treatment of subtypes of leukemia harboring chromosomal translocations. Promising results have been observed in the breast cancer prevention setting, where fenretinide prevention trials have provided a strong rationale for further investigation in young women at high risk for breast cancer. Ongoing phase III randomized trials investigating retinoids in combination with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer aim to definitively characterize the role of retinoids in this tumor type. The limited treatment success observed to date in the prevention and treatment of solid tumors may relate to the frequent epigenetic silencing of RARβ. Robust evaluation of RARβ and downstream genes may permit optimized use of retinoids in the solid tumor arena.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Orfanos CE, Zouboulis CC, Almond-Roesler B, Geilen CC. Current use and future potential role of retinoids in dermatology. Drugs. 1997;53:358–388. - PubMed
-
- Duvic M, Hymes K, Heald P, Breneman D, Martin AG, Myskowski P, et al. Bexarotene is effective and safe for treatment of refractory advanced-stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: multinational phase II-III trial results. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2001;19:2456–2471. - PubMed
-
- Tallman MS, Andersen JW, Schiffer CA, Appelbaum FR, Feusner JH, Ogden A, et al. All-trans-retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia. The New England journal of medicine. 1997;337:1021–1028. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

