Role of nuclear receptor NR4A2 in gastrointestinal inflammation and cancers
- PMID: 23322982
- PMCID: PMC3531668
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.6865
Role of nuclear receptor NR4A2 in gastrointestinal inflammation and cancers
Abstract
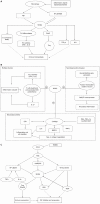
NR4A2 is a transcription factor belonging to the steroid orphan nuclear receptor superfamily. It was originally considered to be essential in the generation and maintenance of dopaminergic neurons, and associated with neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease. Recently, NR4A2 has been found to play a critical role in some inflammatory diseases and cancer. NR4A2 can be efficiently trans-activated by some proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway serves as a principal regulator of inducible NR4A expression in immune cells. NR4A2 can trans-activate Foxp3, a hallmark specifically expressed in regulatory T (Treg) cells, and plays a critical role in the differentiation, maintenance, and function of Treg cells. NR4A2 in T lymphocytes is pivotal for Treg cell induction and suppression of aberrant induction of Th1 under physiological and pathological conditions. High density of Foxp3(+) Treg cells is significantly associated with gastrointestinal inflammation, tumor immune escape, and disease progression. NR4A2 is produced at high levels in CD133(+) colorectal carcinoma (CRC) cells and significantly upregulated by cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin E(2) in a cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)/protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent manner in CRC cells. The cAMP/PKA signaling pathway is the common pathway of NR4A2-related inflammation and cancer. NR4A2 trans-activates osteopontin, a direct target of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway associated with CRC invasion, metastasis, and poor prognosis. Knockdown of endogenous NR4A2 expression attenuates VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration and in vivo angiogenesis. Taken together, NR4A2 emerges as an important nuclear factor linking gastrointestinal inflammation and cancer, especially CRC, and should serve as a candidate therapeutic target for inflammation-related gastrointestinal cancer.
Keywords: Gastrointestinal carcinoma; Immune cells; Inflammation; NR4A2; Signaling pathway.
Figures
References
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

