A systemic complete response of metastatic melanoma to local radiation and immunotherapy
- PMID: 23323154
- PMCID: PMC3542835
- DOI: 10.1593/tlo.12280
A systemic complete response of metastatic melanoma to local radiation and immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: Melanoma is a relatively immunogenic tumor, in which infiltration of melanoma cells by T lymphocytes is associated with a better clinical prognosis. We hypothesized that radiation-induced cell death may provide additional stimulation of an anti-tumor immune response in the setting of anti-CTLA-4 treatment.
Methods: In a pilot melanoma patient, we prospectively tested this hypothesis. We treated the patient with two cycles of ipilimumab, followed by stereotactic ablative radiotherapy to two of seven hepatic metastases, and two additional cycles of ipilimumab.
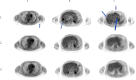
Results: Subsequent positron emission tomography-computed tomography scan indicated that all metastases, including unirradiated liver lesions and an unirradiated axillary lesion, had completely resolved, consistent with a complete response by RECIST.
Conclusion: The use of radiotherapy in combination with targeted immunotherapy as a noninvasive in vivo tumor vaccine strategy appears to be a promising method of enhancing the induction of systemic immune responses and anti-tumor effect.
Figures
References
-
- Clemente CG, Mihm MC, Jr, Bufalino R, Zurrida S, Collini P, Cascinelli N. Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the vertical growth phase of primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer. 1996;77(7):1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:233–258. - PubMed
-
- Walunas TL, Lenschow DJ, Bakker CY, Linsley PS, Freeman GJ, Green JM, Thompson CB, Bluestone JA. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1(5):405–413. - PubMed
-
- Krummel MF, Sullivan TJ, Allison JP. Superantigen responses and co-stimulation: CD28 and CTLA-4 have opposing effects on T cell expansion in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunol. 1996;8(4):519–523. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
