Vitamin D and rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 23323190
- PMCID: PMC3539179
- DOI: 10.1177/2042018812471070
Vitamin D and rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: Vitamin D deficiency has been implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, such as diabetes mellitus type 1 and multiple sclerosis. Reduced vitamin D intake has been linked to increased susceptibility to the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and vitamin D deficiency has been found to be associated with disease activity in patients with RA. The objective was to evaluate vitamin D status in patients with RA and to assess the relationship between vitamin D levels and disease activity.
Methods: In a cohort of 44 patients with RA, 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) [25(OH)D(3)] levels, parathyroid hormone levels, C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were measured. Disease activity was evaluated by calculating the 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28). A control group (n = 44), matched for age and sex, was evaluated as well.
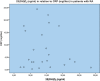
Results: In the cohort of 44 patients with RA 25(OH)D(3) levels were found to be low compared with the control group, 25(OH)D(3) being 15.26 ± 1.07 ng/ml [mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM)] and 25.8 ± 1.6 ng/ml in the patient and control group respectively (Student's t test, p < 0.001). Parathyroid hormone levels were 71.08 ± 7.02 pg/ml (mean ± SEM) (normal values 10.0-65.0 pg/ml), CRP 7.6 ± 1.57 mg/litre (mean ± SEM) (normal values < 3 mg/litre) and ESR was 38.0 ± 4.6 mm/h (mean ± SEM) in the group of patients with RA. Levels of 25(OH)D(3) were found to be negatively correlated to the DAS28, the correlation coefficient being -0.084. Levels of 25(OH)D(3) were also found to be negatively correlated to CRP and ESR, the correlation coefficient being -0.115 and -0.18, respectively.
Conclusion: It appears that vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent in patients with RA, and that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to disease severity in RA. As vitamin D deficiency has been linked to diffuse musculoskeletal pain, these results have therapeutic implications. Vitamin D supplementation may be needed both for the prevention of osteoporosis as well as for pain relief in patients with RA.
Keywords: disease activity; rheumatoid arthritis; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Adorini L. (2005) Intervention in autoimmunity: the potential of vitamin D receptor agonists. Cell Immunol 233: 115–124 - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D., Neogi T., Silman A., Funovits J., Felson D., Bingham C., III, et al. (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62: 2569–2581 - PubMed
-
- Baker J., Baker D., Toedter G., Shults J., Von Feldt J., Leonard M. (2012) Associations between vitamin D, disease activity, and clinical response to therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30: 658–664 - PubMed
-
- Bartels L., Hvas C., Agnholt J., Dahlerup J., Agger R. (2010) Human dendritic cell antigen presentation and chemotaxis are inhibited by intrinsic 25-hydroxy vitamin D activation. Int Immunopharmacol 10: 922–928 - PubMed
-
- Bartley J. (2010) Vitamin D: emerging roles in infection and immunity. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 8: 1359–1369 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

