Hypokalaemia: common things occur commonly - a retrospective survey
- PMID: 23323198
- PMCID: PMC3545329
- DOI: 10.1258/shorts.2012.011179
Hypokalaemia: common things occur commonly - a retrospective survey
Abstract
Objectives: To define the causes of hypokalaemia in an unselected adult population.
Design: Retrospective survey of biochemistry database.
Setting: District general hospital in southwest Scotland.
Participants and main outcome measures: There were 187,704 measurements of urea and electrolytes in 2010. Sixty-one patients had serum potassium <2.5 mmol/L on at least one occasion.
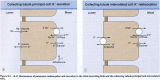
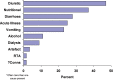
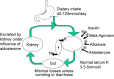
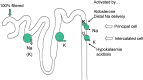
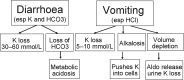
Results: Average age of the patients was 71 (range 33-99) years. The most common causes were diarrhoea and/or vomiting (51% of cases), diuretic therapy (47%), nutritional causes including poor dietary intake, re-feeding syndrome and inadequate potassium supplementation when patients were nil by mouth (37%). In 25% of patients a transient and profound fall in serum potassium appeared to coincide with their acute illness. Acute alcohol intoxication and/or alcohol withdrawal were prominent features in 11% of patients. More than one cause was commonly present. There were no cases of Bartter's, Gitelman's or Liddle's syndromes or of hypokalaemic periodic paralysis in this study.
Conclusions: Severe hypokalaemia <2.5 mmol/L occurs at least once a week in a district general hospital with a catchment population of around 150,000, suggesting there may be around 300 cases a week in the UK (population around 50,000,000). Diuretics, vomiting and diarrhoea are commonly implicated as are nutritional causes, acute illness and alcohol. Bartter's, Gitelman's, Liddle's syndrome and hypokalaemic period paralysis are all extremely uncommon.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Miscellaneous non-inflammatory musculoskeletal conditions. Bartter's and Gitelman's diseases.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Oct;25(5):637-48. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2011.10.013. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 22142744 Review.
-
A case of Gitelman's syndrome presenting with extreme hypokalaemia and paralysis.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2009 Feb;117(2):69-71. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1078705. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 18523931
-
Problems in diagnosing atypical Gitelman's syndrome presenting with normomagnesaemia.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010 Feb;72(2):272-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03649.x. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010. PMID: 19508680
-
Molecular pathophysiology of Bartter's and Gitelman's syndromes.World J Pediatr. 2015 May;11(2):113-25. doi: 10.1007/s12519-015-0016-4. Epub 2015 Mar 9. World J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25754753 Review.
-
Chronic hypokalaemia of adults: Gitelman's syndrome is frequent but classical Bartter's syndrome is rare.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995;10(9):1607-13. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995. PMID: 8559478
Cited by
-
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome: mechanisms, manifestations, and management.Acta Neurol Scand. 2017 Jan;135(1):4-16. doi: 10.1111/ane.12671. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017. PMID: 27586815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum electrolytes disorder and its associated factors among adults admitted with metabolic syndrome in Jimma Medical Center, South West Ethiopia: Facility based crossectional study.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 5;15(11):e0241486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241486. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33152003 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Hypokalemia and Metabolic Alkalosis Caused by Licorice Discovered During the Treatment of Intraoperative Hypoxemia.Cureus. 2022 May 28;14(5):e25432. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25432. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35774714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar P, Clark ML Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine 7th edn Saunders, Edinburgh: Elsevier, 2009
-
- Colledge NR, Walker BR, Ralston SH, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine 21st edn Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh: Elsevier, 2010
-
- Unwin RJ, Luft FC, Shirley DG Pathophysiology and management of hypokalaemia: a clinical prospective. Nat Rev Nephrol 2011;7:75–84 - PubMed
-
- Gennari FJ Hypokalaemia. N Engl J Med 1998;339:451–8 - PubMed
-
- Halperin ML, Kamel KS Potassium. Lancet 1998;352:135–40 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
