Intraspinal ganglion cyst
- PMID: 23323226
- PMCID: PMC3539101
- DOI: 10.4068/cmj.2012.48.3.183
Intraspinal ganglion cyst
Abstract
The pathogenesis of juxtafacet cysts is closely related to degenerative instability of the lumbar spine and degenerative changes in the ligamentum flavum and the facet joint. A 56-year-old man presented with severe right thigh pain and numbness for 1 month after a laminar fracture of the L4 spine. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a heterogenous cystic mass surrounding the facet joint between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae on the right side. Conservative therapy was unsuccessful and the lesion was removed by surgical decompression alone without fusion. The histological examination showed a fragmented, cystic wall-like structure composed of myxoid degenerative tissue without lining epithelium. Here we present this case of a ganglion cyst that appeared to be associated with facet joint instability.
Keywords: Ganglion cysts; Spine; Synovial cyst.
Figures
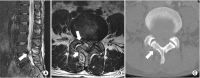

References
-
- Abdullah AF, Chambers RW, Daut DP. Lumbar nerve root compression by synovial cysts of the ligamentum flavum. Report of four cases. J Neurosurg. 1984;60:617–620. - PubMed
-
- Kjerulf TD, Terry DW, Jr, Boubelik RJ. Lumbar synovial or ganglion cysts. Neurosurgery. 1986;19:415–420. - PubMed
-
- Spinner RJ, Hébert-Blouin MN, Maus TP, Atkinson JL, Desy NM, Amrami KK. Evidence that atypical juxtafacet cysts are joint derived. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;12:96–102. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

