In vivo validation of quantitative frequency domain fluorescence tomography
- PMID: 23323291
- PMCID: PMC3525318
- DOI: 10.1117/1.jbo.17.12.126021
In vivo validation of quantitative frequency domain fluorescence tomography
Abstract
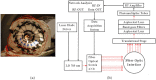
We have developed a hybrid frequency domain fluorescence tomography and magnetic resonance imaging system (MRI) for small animal imaging. The main purpose of this system is to obtain quantitatively accurate fluorescence concentration and lifetime images using a multi-modality approach. In vivo experiments are undertaken to evaluate the system. We compare the recovered fluorescence parameters with and without MRI structural a priori information. In addition, we compare two optical background heterogeneity correction methods: Born normalization and utilizing diffuse optical tomography (DOT) functional a priori information. The results show that the concentration and lifetime of a 4.2-mm diameter indocyanine green inclusion located 15 mm deep inside a rat can be recovered with less than a 5% error when functional a priori information from DOT and structural a priori information from MRI are utilized.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

