Intelligent design of multifunctional lipid-coated nanoparticle platforms for cancer therapy
- PMID: 23323560
- PMCID: PMC3584330
- DOI: 10.4155/tde.12.127
Intelligent design of multifunctional lipid-coated nanoparticle platforms for cancer therapy
Abstract
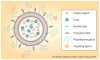
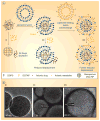
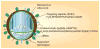
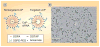
Nanotechnology is rapidly evolving and dramatically changing the paradigms of drug delivery. The small sizes, unique chemical properties, large surface areas, structural diversity and multifunctionality of nanoparticles prove to be greatly advantageous for combating notoriously therapeutically evasive diseases such as cancer. Multifunctional nanoparticles have been designed to enhance tumor uptake through either passive or active targeting, while also avoiding reticuloendothelial system uptake through the incorporation of PEG onto the surface. First-generation nanoparticle systems, such as liposomes, are good carriers for drugs and nucleic acid therapeutics, although they have some limitations. These lipid bilayers are now being utilized as excellent carriers for drug-loaded, solid core particles such as iron oxide, mesoporus silica and calcium phosphate. In this article, their design, as well as their multifunctional role in cancer therapy are discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Sinha R, Kim GJ, Nie S, Shin DM. Nanotechnology in cancer therapeutics: bioconjugated nanoparticles for drug delivery. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5(8):1909–1917. - PubMed
-
- Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011;331(6024):1559–1564. - PubMed
-
- Marshall E. Cancer research and the $90 billion metaphor. Science. 2011;331(6024):1540–1541. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Gu FX, Chan JM, Wang AZ, Langer RS, Farokhzad OC. Nanoparticles in medicine: therapeutic applications and developments. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008;83(5):761–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
