Single-cell lipidomics: characterizing and imaging lipids on the surface of individual Aplysia californica neurons with cluster secondary ion mass spectrometry
- PMID: 23323749
- PMCID: PMC3867296
- DOI: 10.1021/ac303038j
Single-cell lipidomics: characterizing and imaging lipids on the surface of individual Aplysia californica neurons with cluster secondary ion mass spectrometry
Abstract
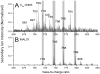
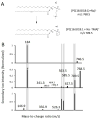
Neurons isolated from Aplysia californica , an organism with a well-defined neural network, were imaged with secondary ion mass spectrometry, C(60)-SIMS. A major lipid component of the neuronal membrane was identified as 1-hexadecyl-2-octadecenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine [PC(16:0e/18:1)] using tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). The assignment was made directly off the sample surface using a C(60)-QSTAR instrument, a prototype instrument that combines an ion source with a commercial electrospray ionization/matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (ESI/MALDI) mass spectrometer. Normal phase liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (NP-LC-MS) was used to confirm the assignment. Cholesterol and vitamin E were also identified with in situ tandem MS analyses that were compared to reference spectra obtained from purified compounds. In order to improve sensitivity on the single-cell level, the tandem MS spectrum of vitamin E reference material was used to extract and compile all the vitamin E related peaks from the cell image. The mass spectrometry images reveal heterogeneous distributions of intact lipid species, PC(16:0e/18:1), vitamin E, and cholesterol on the surface of a single neuron. The ability to detect these molecules and determine their relative distribution on the single-cell level shows that the C(60)-QSTAR is a potential platform for studying important biochemical processes, such as neuron degeneration.
Figures


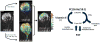
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

