A parallel, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to investigate the effect of SagaPro on nocturia in men
- PMID: 23323790
- PMCID: PMC3549610
- DOI: 10.3109/00365599.2012.695390
A parallel, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to investigate the effect of SagaPro on nocturia in men
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effect of SagaPro, a product derived from Angelica archangelica leaf, on nocturia.
Material and methods: Sixty-nine male patients 45 years or older with at least two nocturnal voids were randomized to receive SagaPro or placebo in a double-blind design for 8 weeks. Voiding diaries were assessed before and after the treatment.
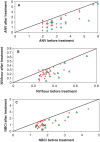
Results: The results indicate that SagaPro is safe. The actual number of nocturnal voids (ANV), nocturnal polyuria index (NPi) and nocturnal bladder capacity index (NBC index) decreased in the test population, but there was no significant difference between the treatment groups. Subsequent subgroup analysis showed that SagaPro significantly reduced the NBC index and nocturnal voids per sleeping hour in comparison to the placebo in participants with baseline NBC index above 1.3. When participants with sleep disorders were excluded from this group, ANV was also significantly reduced for the SagaPro group in comparison to the placebo group.
Conclusion: SagaPro, made from an extract of the medicinal herb Angelica archangelica, is safe. This study did not show that SagaPro improved nocturia overall compared to placebo. Subgroup analysis suggested a beneficial effect in individuals with decreased nocturnal bladder capacity, which warrants further study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigations on the constituents of SagaPro tablets, a food supplement manufactured from Angelica archangelica leaf.Pharmazie. 2017 Jan 10;72(1):3-4. doi: 10.1691/ph.2017.6807. Pharmazie. 2017. PMID: 29441889
-
Efficacy and safety of low dose desmopressin orally disintegrating tablet in women with nocturia: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, parallel group study.J Urol. 2013 Sep;190(3):958-64. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.02.037. Epub 2013 Feb 20. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23454404 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of novel β3 -adrenoreceptor agonist vibegron on nocturia in patients with overactive bladder: A post-hoc analysis of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study.Int J Urol. 2019 Mar;26(3):369-375. doi: 10.1111/iju.13877. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Int J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30557916 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Desmopressin for treating nocturia in men.BJU Int. 2018 Oct;122(4):549-559. doi: 10.1111/bju.14183. Epub 2018 Mar 26. BJU Int. 2018. PMID: 29489052
-
Terminology, epidemiology, etiology, and pathophysiology of nocturia.Neurourol Urodyn. 2014 Apr;33 Suppl 1:S2-5. doi: 10.1002/nau.22595. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014. PMID: 24729150 Review.
Cited by
-
Urox containing concentrated extracts of Crataeva nurvala stem bark, Equisetum arvense stem and Lindera aggregata root, in the treatment of symptoms of overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind placebo controlled trial.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jan 31;18(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2101-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29385990 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Herbal fertility treatments used in North America from colonial times to 1900, and their potential for improving the success rate of assisted reproductive technology.Reprod Biomed Soc Online. 2018 Apr 12;5:60-81. doi: 10.1016/j.rbms.2018.03.001. eCollection 2018 Apr. Reprod Biomed Soc Online. 2018. PMID: 30023440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Staskin D, Kelleher C, Avery K, Bosch R, Cotterill N, Coyne K, et al. Initial assessment of urinary and faecal incontinence in adult male and female patients. In: Abrams P, Cardozo L, Khoury S, Wein A, editors. Incontinence. 4th ed. Plymouth: Health Publications; 2009.
-
- Tikkinen KA, Johnson TM, Tammela TL, Sintonen H, Haukka J, Huhtala H, et al. Nocturia frequency, bother, and quality of life: how often is too often? A population-based study in Finland. Eur Urol. 2010;57:488–96. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Kastler E, Tubaro A. The measurement of nocturia and its impact on quality of sleep and quality of life in LUTS/BPH. Eur Urol Suppl. 2006;5:3–11.
-
- Weiss JP, Blaivas JG. Nocturia. J Urol. 2000;163:5–12. - PubMed
-
- Udo Y, Nakao M, Honjo H, Ukimura O, Kawauchi A, Kitakoji H, et al. Analysis of nocturia with 24-h urine volume, nocturnal urine volume, nocturnal bladder capacity and length of sleep duration: concept for effective treatment modality. BJU Int. 2011;107:791–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
