Inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3β by AKT, PKA, and PI3K contributes to high NaCl-induced activation of the transcription factor NFAT5 (TonEBP/OREBP)
- PMID: 23324178
- PMCID: PMC3625851
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00591.2012
Inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3β by AKT, PKA, and PI3K contributes to high NaCl-induced activation of the transcription factor NFAT5 (TonEBP/OREBP)
Abstract
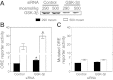
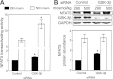
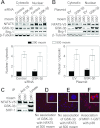
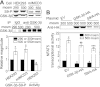
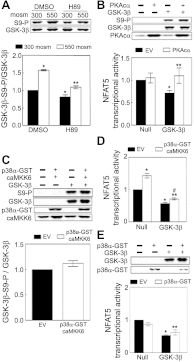
High NaCl activates the transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 (NFAT5), leading to increased transcription of osmoprotective target genes. Kinases PKA, PI3K, AKT1, and p38α were known to contribute to the high NaCl-induced increase of NFAT5 activity. We now identify another kinase, GSK-3β. siRNA-mediated knock-down of GSK-3β increases NFAT5 transcriptional and transactivating activities without affecting high NaCl-induced nuclear localization of NFAT5 or NFAT5 protein expression. High NaCl increases phosphorylation of GSK-3β-S9, which inhibits GSK-3β. In GSK-3β-null mouse embryonic fibroblasts transfection of GSK-3β, in which serine 9 is mutated to alanine, so that it cannot be inhibited by phosphorylation at that site, inhibits high NaCl-induced NFAT5 transcriptional activity more than transfection of wild-type GSK-3β. High NaCl-induced phosphorylation of GSK-3β-S9 depends on PKA, PI3K, and AKT, but not p38α. Overexpression of PKA catalytic subunit α or of catalytically active AKT1 reduces inhibition of NFAT5 by GSK-3β, but overexpression of p38α together with its catalytically active upstream kinase, MKK6, does not. Thus, GSK-3β normally inhibits NFAT5 by suppressing its transactivating activity. When activated by high NaCl, PKA, PI3K, and AKT1, but not p38α, increase phosphorylation of GSK-3β-S9, which reduces the inhibitory effect of GSK-3β on NFAT5, and thus contributes to activation of NFAT5.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rac1/osmosensing scaffold for MEKK3 contributes via phospholipase C-gamma1 to activation of the osmoprotective transcription factor NFAT5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 19;108(29):12155-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1108107108. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21712438 Free PMC article.
-
High NaCl-induced activation of CDK5 increases phosphorylation of the osmoprotective transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP at threonine 135, which contributes to its rapid nuclear localization.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Mar 1;22(5):703-14. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-08-0681. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21209322 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviating the suppression of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta by Akt leads to the phosphorylation of cAMP-response element-binding protein and its transactivation in intact cell nuclei.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 17;278(42):41338-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302972200. Epub 2003 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12900420
-
Genetic deletion of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta abrogates activation of IkappaBalpha kinase, JNK, Akt, and p44/p42 MAPK but potentiates apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 17;279(38):39541-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403449200. Epub 2004 Jul 13. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15252041
-
Troglitazone ameliorates high glucose-induced EMT and dysfunction of SGLTs through PI3K/Akt, GSK-3β, Snail1, and β-catenin in renal proximal tubule cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):F1263-75. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00475.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20015942
Cited by
-
Understanding Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3: A Novel Avenue for Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):4203-4221. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03839-1. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38064104 Review.
-
Potential Role of Gene Regulator NFAT5 in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Sep 15;2020:6927429. doi: 10.1155/2020/6927429. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 33015193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of (pro)renin receptor expression in mIMCD via the GSK-3β-NFAT5-SIRT-1 signaling pathway.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Sep 1;307(5):F593-600. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00245.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24990896 Free PMC article.
-
A massively parallel reporter assay library to screen short synthetic promoters in mammalian cells.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 28;15(1):10353. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54502-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39609378 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II type 2 receptor activation preserves megalin in the kidney and prevents proteinuria in high salt diet fed rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 15;13(1):4277. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31454-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36922642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beals CR, Clipstone NA, Ho SN, Crabtree GR. Nuclear localization of NF-ATc by a calcineurin-dependent, cyclosporin-sensitive intramolecular interaction. Genes Dev 11: 824–834, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Beals CR, Sheridan CM, Turck CW, Gardner P, Crabtree GR. Nuclear export of NF-ATc enhanced by glycogen synthase kinase-3. Science 275: 1930–1934, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Burg MB, Ferraris JD, Dmitrieva NI. Cellular response to hyperosmotic stresses. Physiol Rev 87: 1441–1474, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

