The efficacy of L. (L.) chagasi excreted-secreted antigens (ESAs) for visceral leishmaniasis diagnosis is due to low levels of cross-reactivity
- PMID: 23324219
- PMCID: PMC3592541
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.12-0587
The efficacy of L. (L.) chagasi excreted-secreted antigens (ESAs) for visceral leishmaniasis diagnosis is due to low levels of cross-reactivity
Abstract
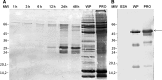
The analysis of promastigote excreted-secreted antigen (ESA) reactivity with 53 visceral leishmaniasis (VL) cases showed that each sample reacted regardless of the antigen or the Leishmania species used in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) displayed 100% positivity with the L. (L.) chagasi ESA-blot recognizing bands of molecular weight ranging from 26.5 to 31.5 kDa. The analysis of 160 non-visceral cases showed that 5% of the samples cross-reacted with the L. (L.) chagasi ESA-ELISA and 9.4% reacted with the ESA isolated from L. (L.) amazonensis and L. (V.) braziliensis, whereas a high cross-reaction ranging from 24.4% to 25% was observed with total crude promastigote antigens (PRO-ELISA). The ESA-blot of L. (L.) chagasi tested with non-visceral sera samples showed a cross-reaction with 8.8% of cases; most of these cases represented tegumentary leishmaniasis and only one acute chagasic case. These data lead us to recommend the use of ESA as an alternative antigen in VL diagnosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Montenegro's skin reactions and antibodies against different Leishmania species in dogs from a visceral leishmaniosis endemic area.Vet Parasitol. 2006 Jun 30;139(1-3):21-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.02.033. Epub 2006 Mar 29. Vet Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16567046
-
New insights about cross-reactive epitopes of six trypanosomatid genera revealed that Crithidia and Leptomonas have antigenic similarity to L. (L.) chagasi.Acta Trop. 2014 Mar;131:41-6. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.11.010. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Acta Trop. 2014. PMID: 24275757
-
An ELISA immunoassay employing a conserved Leishmania hypothetical protein for the serodiagnosis of visceral and tegumentary leishmaniasis in dogs and humans.Cell Immunol. 2017 Aug;318:42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Cell Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28602279
-
Evaluation of Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum excreted-secreted antigens for detection of canine leishmaniasis.Acta Trop. 2016 Sep;161:41-3. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 19. Acta Trop. 2016. PMID: 27212707
-
Challenges in the diagnosis of post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis.Indian J Med Res. 2006 Mar;123(3):295-310. Indian J Med Res. 2006. PMID: 16778312 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Four Leishmania infantum Potentially Excreted/Secreted Proteins on Human Dendritic Cells Differentiation and Maturation.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 18;10(11):e0143063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143063. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26581100 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of recombinant K39 antigen and various promastigote antigens in sero-diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in Bangladesh.Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2016 Jul 30;1(3):219-228. doi: 10.1016/j.parepi.2016.07.003. eCollection 2016 Sep. Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2016. PMID: 29988192 Free PMC article.
-
Leptomonas seymouri and Crithidia fasciculata exoantigens can discriminate human cases of visceral leishmaniasis from American tegumentary leishmaniasis ones.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2017 Apr 3;59:e1. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946201759001. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2017. PMID: 28380110 Free PMC article.
-
Field validation of a Leishmania (Leishmania) mexicana exo-antigens ELISA for diagnosing tegumentary leishmaniasis in regions of Leishmania (Viannia) predominance.Braz J Infect Dis. 2015 May-Jun;19(3):302-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 May 15. Braz J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25985901 Free PMC article.
-
Leishmania infantum exo-antigens: application toward serological diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis.Parasitol Res. 2019 Jul;118(7):2317-2323. doi: 10.1007/s00436-019-06352-4. Epub 2019 May 29. Parasitol Res. 2019. PMID: 31144033
References
-
- Srividya G, Kulshrestha A, Singh R, Salotra P. Diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis: developments over the last decade. Parasitol Res. 2012;110:1065–1078. - PubMed
-
- Momen H, Grimaldi Júnior G, Deane LM. Leishmania infantum, the etiological agent of American visceral leishmaniasis (AVL)? Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1987;82:447–448. - PubMed
-
- Martin SK, Thuita-Harun L, Adoyo-Adoyo M, Wasunna KM. A diagnostic ELISA for visceral leishmaniasis, based on antigen from media conditioned by Leishmania donovani promastigotes. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1998;92:571–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

