Functionalization of gadolinium metallofullerenes for detecting atherosclerotic plaque lesions by cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- PMID: 23324435
- PMCID: PMC3562260
- DOI: 10.1186/1532-429X-15-7
Functionalization of gadolinium metallofullerenes for detecting atherosclerotic plaque lesions by cardiovascular magnetic resonance
Abstract
Background: The hallmark of atherosclerosis is the accumulation of plaque in vessel walls. This process is initiated when monocytic cells differentiate into macrophage foam cells under conditions with high levels of atherogenic lipoproteins. Vulnerable plaque can dislodge, enter the blood stream, and result in acute myocardial infarction and stroke. Imaging techniques such as cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) provides one strategy to identify patients with plaque accumulation.
Methods: We synthesized an atherosclerotic-targeting contrast agent (ATCA) in which gadolinium (Gd)-containing endohedrals were functionalized and formulated into liposomes with CD36 ligands intercalated into the lipid bilayer. In vitro assays were used to assess the specificity of the ATCA for foam cells. The ability of ATCA to detect atherosclerotic plaque lesions in vivo was assessed using CMR.
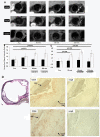
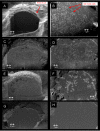
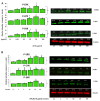
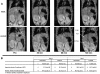
Results: The ATCA was able to detect scavenger receptor (CD36)-expressing foam cells in vitro and were specifically internalized via the CD36 receptor as determined by focused ion beam/scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) and Western blotting analysis of CD36 receptor-specific signaling pathways. The ATCA exhibited time-dependent accumulation in atherosclerotic plaque lesions of ApoE -/- mice as determined using CMR. No ATCA accumulation was observed in vessels of wild type (C57/b6) controls. Non-targeted control compounds, without the plaque-targeting moieties, were not taken up by foam cells in vitro and did not bind plaque in vivo. Importantly, the ATCA injection was well tolerated, did not demonstrate toxicity in vitro or in vivo, and no accumulation was observed in the major organs.
Conclusions: The ATCA is specifically internalized by CD36 receptors on atherosclerotic plaque providing enhanced visualization of lesions under physiological conditions. These ATCA may provide new tools for physicians to non-invasively detect atherosclerotic disease.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

