The archaeal DnaG protein needs Csl4 for binding to the exosome and enhances its interaction with adenine-rich RNAs
- PMID: 23324612
- PMCID: PMC3672285
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.23450
The archaeal DnaG protein needs Csl4 for binding to the exosome and enhances its interaction with adenine-rich RNAs
Abstract
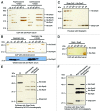
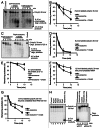
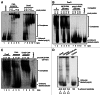
The archaeal RNA-degrading exosome contains a catalytically active hexameric core, an RNA-binding cap formed by Rrp4 and Csl4 and the protein annotated as DnaG (bacterial type primase) with so-far-unknown functions in RNA metabolism. We found that the archaeal DnaG binds to the Csl4-exosome but not to the Rrp4-exosome of Sulfolobus solfataricus. In vitro assays revealed that DnaG is a poly(A)-binding protein enhancing the degradation of adenine-rich transcripts by the Csl4-exosome. DnaG is the second poly(A)-binding protein besides Rrp4 in the heteromeric, RNA-binding cap of the S. solfataricus exosome. This apparently reflects the need for effective and selective recruitment of adenine-rich RNAs to the exosome in the RNA metabolism of S. solfataricus.
Keywords: DnaG; RNA binding; archaea; exosome; poly(A) binding.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enzymatic Analysis of Reconstituted Archaeal Exosomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2062:63-79. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9822-7_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31768972
-
Archaeal DnaG contains a conserved N-terminal RNA-binding domain and enables tailing of rRNA by the exosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Nov 10;42(20):12691-706. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku969. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25326320 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of the archaeal exosome.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 Sep-Oct;5(5):623-35. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1234. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24789718 Review.
-
Heterogeneous complexes of the RNA exosome in Sulfolobus solfataricus.Biochimie. 2012 Jul;94(7):1578-87. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.03.026. Epub 2012 Apr 7. Biochimie. 2012. PMID: 22503705
-
The archaeal exosome.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;702:29-38. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 21618872 Review.
Cited by
-
Enzymatic Analysis of Reconstituted Archaeal Exosomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2062:63-79. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9822-7_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31768972
-
Global phylogenomic analysis disentangles the complex evolutionary history of DNA replication in archaea.Genome Biol Evol. 2014 Jan;6(1):192-212. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu004. Genome Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24398374 Free PMC article.
-
sRNA154 a newly identified regulator of nitrogen fixation in Methanosarcina mazei strain Gö1.RNA Biol. 2017 Nov 2;14(11):1544-1558. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1306170. Epub 2017 Apr 27. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28296572 Free PMC article.
-
The SmAP1/2 proteins of the crenarchaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus interact with the exosome and stimulate A-rich tailing of transcripts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jul 27;45(13):7938-7949. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx437. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28520934 Free PMC article.
-
RNA processing machineries in Archaea: the 5'-3' exoribonuclease aRNase J of the β-CASP family is engaged specifically with the helicase ASH-Ski2 and the 3'-5' exoribonucleolytic RNA exosome machinery.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 17;48(7):3832-3847. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa052. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32030412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farhoud MH, Wessels HJ, Steenbakkers PJ, Mattijssen S, Wevers RA, van Engelen BG, et al. Protein complexes in the archaeon Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus analyzed by blue native/SDS-PAGE and mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005;4:1653–63. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M500171-MCP200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
