Activation of NK cells by HIV-specific ADCC antibodies: role for granulocytes in expressing HIV-1 peptide epitopes
- PMID: 23324623
- PMCID: PMC3899135
- DOI: 10.4161/hv.23446
Activation of NK cells by HIV-specific ADCC antibodies: role for granulocytes in expressing HIV-1 peptide epitopes
Abstract
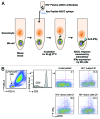
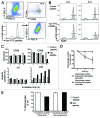
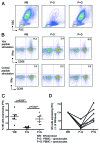
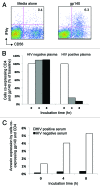
HIV-specific ADCC antibodies could play a role in providing protective immunity. We have developed a whole blood ADCC assay that measures NK cell activation in response to HIV peptide epitopes. These HIV peptide-specific ADCC responses are associated with escape from immune recognition and slower progression of HIV infection and represent interesting HIV vaccine antigens. However, the mechanism by which these epitopes are expressed and whether or not they induce NK-mediated killing of cells expressing such peptide-antigens is not understood. Herein, we show that fluorescent-tagged ADCC peptide epitopes associate with blood granulocytes. The peptide-associated granulocytes become a specific target for antibody-mediated killing, as shown by enhanced expression of apoptosis marker Annexin and reduction in cell numbers. When HIV Envelope gp140 protein is utilized in the ADCC assay, we detected binding to its ligand, CD4. During the incubation, cells co-expressing gp140 and CD4 reduce in number. We also detected increasing Annexin expression in these cells. These data indicate that blood cells expressing HIV-specific ADCC epitopes are targeted for killing by NK cells in the presence of ADCC antibodies in HIV+ plasma and provide a clearer framework to evaluate these antigens as vaccine candidates.
Keywords: ADCC; Apoptosis; Granulocytes; HIV; NK cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NK cell function and antibodies mediating ADCC in HIV-1-infected viremic and controller patients.Viral Immunol. 2011 Oct;24(5):359-68. doi: 10.1089/vim.2011.0025. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Viral Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21958370
-
Rapid degranulation of NK cells following activation by HIV-specific antibodies.J Immunol. 2009 Jan 15;182(2):1202-10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.2.1202. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19124764
-
The Early Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Response Is Associated With Lower Viral Set Point in Individuals With Primary HIV Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 9;9:2322. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02322. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30356637 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-specific antibody immunity mediated through NK cells and monocytes.Curr HIV Res. 2013 Jul;11(5):388-406. doi: 10.2174/1570162x113116660061. Curr HIV Res. 2013. PMID: 24191935 Review.
-
Obstacles to ideal anti-HIV antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses.Vaccine. 2013 Nov 12;31(47):5506-17. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.035. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23981432 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural killer cells in HIV-1 infection and therapy.AIDS. 2017 Nov 13;31(17):2317-2330. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001645. AIDS. 2017. PMID: 28926399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-dependent CD56+ T cell responses are functionally impaired in long-term HIV-1 infection.Retrovirology. 2016 Nov 4;13(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12977-016-0313-6. Retrovirology. 2016. PMID: 27814766 Free PMC article.
-
Combining a rhesus cytomegalovirus/SIV vaccine with a neutralizing antibody to protect against SIV challenges in rhesus macaques.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1592647. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1592647. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40529575 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal Antibody 2C6 Targets a Cross-Clade Conformational Epitope in gp41 with Highly Active Antibody-Dependent Cell Cytotoxicity.J Virol. 2019 Aug 13;93(17):e00772-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00772-19. Print 2019 Sep 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31217246 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza A Virus Antibodies with Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Function.Viruses. 2020 Mar 1;12(3):276. doi: 10.3390/v12030276. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32121563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baum LL, Cassutt KJ, Knigge K, Khattri R, Margolick J, Rinaldo C, et al. HIV-1 gp120-specific antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity correlates with rate of disease progression. J Immunol. 1996;157:2168–73. - PubMed
-
- Ljunggren K, Chiodi F, Biberfeld G, Norrby E, Jondal M, Fenyö EM. Lack of cross-reaction in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity between human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and HIV-related West African strains. J Immunol. 1988;140:602–5. - PubMed
-
- Rook AH, Lane HC, Folks T, McCoy S, Alter H, Fauci AS. Sera from HTLV-III/LAV antibody-positive individuals mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against HTLV-III/LAV-infected T cells. J Immunol. 1987;138:1064–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
