Adult zebrafish as a model system for cutaneous wound-healing research
- PMID: 23325040
- PMCID: PMC3644348
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2013.16
Adult zebrafish as a model system for cutaneous wound-healing research
Abstract
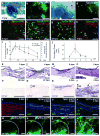
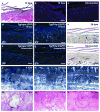
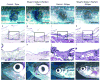
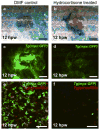
Upon injury, the skin must quickly regenerate to regain its barrier function. In mammals, wound healing is rapid and scar free during embryogenesis, whereas in adults it involves multiple steps including blood clotting, inflammation, re-epithelialization, vascularization, and granulation tissue formation and maturation, resulting in a scar. We have established a rapid and robust method to introduce full-thickness wounds onto the flank of adult zebrafish, and show that apart from external fibrin clot formation, all steps of adult mammalian wound repair also exist in zebrafish. Wound re-epithelialization is extremely rapid and initiates with no apparent lag phase, subsequently followed by the immigration of inflammatory cells and the formation of granulation tissue, consisting of macrophages, fibroblasts, blood vessels, and collagen. The granulation tissue later regresses, resulting in minimal scar formation. Studies after chemical treatment or with transgenic fish further suggest that wound re-epithelialization occurs independently of inflammation and fibroblast growth factor signaling, whereas both are essential for fibroblast recruitment and granulation tissue formation. Together, these results demonstrate that major steps and principles of cutaneous wound healing are conserved among adult mammals and adult zebrafish, making zebrafish a valuable model for studying vertebrate skin repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS, Brem H, Tomic-Canic M. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16:585–601. - PubMed
-
- Broadley KN, Aquino AM, Woodward SC, Buckley-Sturrock A, Sato Y, Rifkin DB, et al. Monospecific antibodies implicate basic fibroblast growth factor in normal wound repair. Lab Invest. 1989;61:571–575. - PubMed
-
- Caddy J, WIlanowski T, Darido C, Dworkin S, Ting SB, Zhao Q, Rank G, Auden A, Srivastava S, Papenfuss TA, Murdoch JN, Humbert PO, Parekh V, Boulos N, Weber T, Zuo J, Cunningham JM, Jane SM. Epidermal wound repair is regulated by the planar cell polarity signaling pathway. Dev Cell. 2010;19:138–47. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dovi JV, He LK, DiPietro LA. Accelerated wound closure in neutrophil-depleted mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;73:448–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

