Ligand binding affinities of arctigenin and its demethylated metabolites to estrogen receptor alpha
- PMID: 23325100
- PMCID: PMC6269892
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules18011122
Ligand binding affinities of arctigenin and its demethylated metabolites to estrogen receptor alpha
Abstract
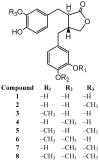
Phytoestrogens are defined as plant-derived compounds with estrogen-like activities according to their chemical structures and activities. Plant lignans are generally categorized as phytoestrogens. It was reported that (-)-arctigenin, the aglycone of arctiin, was demethylated to (-)-dihydroxyenterolactone (DHENL) by Eubacterium (E.) sp. ARC-2. Through stepwise demethylation, E. sp. ARC-2 produced six intermediates, three mono-desmethylarctigenins and three di-desmethylarctigenins. In the present study, ligand binding affinities of (-)-arctigenin and its seven metabolites, including DHENL, were investigated for an estrogen receptor alpha, and found that demethylated metabolites had stronger binding affinities than (-)-arctigenin using a ligand binding screen assay method. The IC(50) value of (2R,3R)-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-3-(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl)-butyrolactone was 7.9 × 10⁻⁴ M.
Figures
References
-
- Rowland I., Faughnan M., Hoey L., Wahala K., Williamson G., Cassidy A. Bioavailability of phyto-oestrogens. Br. J. Nutr. 2003;89:S45–S58. - PubMed
-
- Jin J.S., Tobo T., Chung M.H., Ma C.M., Hattori M. Transformation of trachelogenin, an aglycone of tracheloside from safflower seeds, to phytoestrogenic (−)-enterolactone by human intestinal bacteria. Food Chem. 2012;134:74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.060. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources