Bioassay-guided isolation of DPP-4 inhibitory fractions from extracts of submerged cultured of Inonotus obliquus
- PMID: 23325103
- PMCID: PMC6270506
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules18011150
Bioassay-guided isolation of DPP-4 inhibitory fractions from extracts of submerged cultured of Inonotus obliquus
Abstract
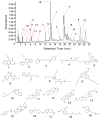
Inonotus obliquus is a medicinal mushroom used in Russian and Eastern European folk medicine for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancer, cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Previous studies in our laboratory have demonstrated that the mycelium powders of I. obliquus possess significant antihyperglycemic effects in a mouse model of diabetic disease induced by alloxan. However, the active ingredients of mycelium powders responsible for the diabetes activity have not been identified. This study aims to identify the active ingredients of I. obliquus mycelium powders by a bioassay-guided fractionation approach and explore the mechanism of action of these active ingredients by using a well-established DPP-4 (an important enzyme as a new therapeutic target for diabetes) inhibitory assay model. The results showed the chloroform extract of mycelium was potential inhibitory against DPP-4. Bioactivity guided fractionation led to the identification of 19 compounds using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Molecular docking between the compounds and DPP-4 revealed that compounds 5, 8, 9, 14, 15 may be the active components responsible for the DPP-4 inhibitory activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A dipyrrole derivative from Aloe vera inhibits an anti-diabetic drug target Dipeptidyl Peptidase (DPP)-IV in vitro.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2020;50(5):511-520. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2019.1710712. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31910723
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV Inhibitory activity of Terminalia arjuna attributes to its cardioprotective effects in experimental diabetes: In silico, in vitro and in vivo analyses.Phytomedicine. 2019 Apr;57:158-165. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.195. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30668318
-
Finding a Potential Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitor for Type-2 Diabetes Treatment Based on Molecular Docking, Pharmacophore Generation, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 13;17(6):920. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060920. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27304951 Free PMC article.
-
Plant dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors as antidiabetic agents: a brief review.Future Med Chem. 2018 May 1;10(10):1229-1239. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0235. Epub 2018 May 11. Future Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29749760 Review.
-
Recent progress of the development of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 May 10;151:145-157. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.041. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29609120 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic stimulation of GLP-1 and GIP protein with DPP-4 inhibitors for type-2 diabetes treatment.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015 Mar 19;14:15. doi: 10.1186/s40200-015-0143-4. eCollection 2015. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015. Retraction in: J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016 Aug 30;15(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40200-016-0256-4. PMID: 26473146 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The protective effects of alpha-pinene on high glucose-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in HepG2 cells.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(8):967-974. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.74546.16191. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38911237 Free PMC article.
-
Chemometrics Optimized Extraction Procedures, Phytosynergistic Blending and in vitro Screening of Natural Enzyme Inhibitors Amongst Leaves of Tulsi, Banyan and Jamun.Pharmacogn Mag. 2015 Oct;11(Suppl 4):S522-32. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.172956. Pharmacogn Mag. 2015. PMID: 27013789 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of natural enzyme inhibitors with hypoglycemic potentials amongst Eucalyptus Spp. by in vitro assays.World J Diabetes. 2014 Apr 15;5(2):209-18. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i2.209. World J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24748933 Free PMC article.
-
α-Amylase and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitory effects of Melicope latifolia bark extracts and identification of bioactive constituents using in vitro and in silico approaches.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):964-973. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1948065. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34347568 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

