Activity-dependent neuronal signalling and autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 23325215
- PMCID: PMC3576027
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11860
Activity-dependent neuronal signalling and autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
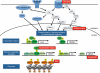
Neuronal activity induces the post-translational modification of synaptic molecules, promotes localized protein synthesis within dendrites and activates gene transcription, thereby regulating synaptic function and allowing neuronal circuits to respond dynamically to experience. Evidence indicates that many of the genes that are mutated in autism spectrum disorder are crucial components of the activity-dependent signalling networks that regulate synapse development and plasticity. Dysregulation of activity-dependent signalling pathways in neurons may, therefore, have a key role in the aetiology of autism spectrum disorder.
Figures



References
-
- Baird G, et al. Prevalence of disorders of the autism spectrum in a population cohort of children in South Thames: the Special Needs and Autism Project (SNAP) Lancet. 2006;368:210–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

