The rod pathway of the microbat retina has bistratified rod bipolar cells and tristratified AII amacrine cells
- PMID: 23325239
- PMCID: PMC6704856
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2072-12.2013
The rod pathway of the microbat retina has bistratified rod bipolar cells and tristratified AII amacrine cells
Abstract
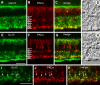
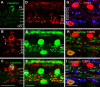
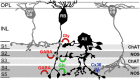
We studied the retinal rod pathway of Carollia perspicillata and Glossophaga soricina, frugivorous microbats of the phyllostomid family. Protein kinase Cα (PKCα) immunolabeling revealed abundant rod bipolar cells (RBCs) with axon terminals in the innermost sublamina of the inner plexiform layer (IPL), which is typical for mammals. Extraordinarily, the RBC axons showed additional synaptic contacts in a second sublamina further out in the IPL. Dye injections of PKCα-prelabeled RBCs of C. perspicillata confirmed the bistratified axon morphology. The functional partition of the IPL into ON and OFF sublayers was shown by using antibodies against vesicular glutamate transporter 1 [labeling all ON and OFF bipolar cell (BC) axon terminals] and G-protein γ13 (labeling all ON BCs). The ON sublayer occupied 75% of the IPL thickness, including both strata of the RBC axons. RBC output onto putative AII amacrine cells (ACs), the crucial interneurons of the rod pathway, was identified by calretinin, PKCα, and CtBP2 triple immunolabeling. Dye injections of calretinin-prelabeled ACs revealed tristratification of the AII ACs corresponding to the bistratified RBCs. Triple immunolabeling for PKCα, nitric oxide synthetase (NOS), and either GABA(C) or CtBP2 indicated GABAergic feedback onto RBCs via NOS-immunoreactive ACs. AII output analysis showed glycineric synapses with glycine receptor α1 expression between AII cells and OFF cone BCs and connexin 36-labeled gap junctions between AII cells and ON cone BCs. We conclude that microbats have a well developed rod pathway with great similarities to that of other mammals, but with an unusual IPL stratification pattern of RBCs and AIIs.
Figures




References
-
- Altringham JD, Fenton MB. Sensory ecology and communication in the chiroptera. In: Kunz TH, Fenton MB, editors. Bat ecology. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press; 2003. pp. 90–127.
-
- Ammermüller J, Kolb H. The organization of the turtle inner retina. I. ON- and OFF-center pathways. J Comp Neurol. 1995;358:1–34. - PubMed
-
- Barton RA, Harvey PH. Mosaic evolution of brain structure in mammals. Nature. 2000;405:1055–1058. - PubMed
-
- Barton RA, Purvis A, Harvey PH. Evolutionary radiation of visual and olfactory brain systems in primates, bats and insectivores. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1995;348:381–392. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield SA, Dacheux RF. Rod vision: pathways and processing in the mammalian retina. Prog Ret Eye Res. 2001;20:351–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
