Carry-over of aflatoxin B1 to aflatoxin M1 in high yielding Israeli cows in mid- and late-lactation
- PMID: 23325299
- PMCID: PMC3564076
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins5010173
Carry-over of aflatoxin B1 to aflatoxin M1 in high yielding Israeli cows in mid- and late-lactation
Abstract
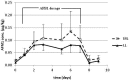
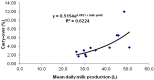
The potent hepatotoxin and carcinogen aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) is a common mycotoxin contaminant of grains used in animal feeds. Aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) is the major metabolite of AFB1 in mammals, being partially excreted into milk, and is a possible human carcinogen. The maximum permitted concentration of AFM1 in cows' milk is 0.05 μg/kg in Israel and the European Union. Since milk yield and the carry-over of AFB1 in the feed to AFM1 in the milk are highly correlated, it was considered important to determine the AFM1 carry-over in Israeli-Holstein dairy cows, distinguished by world record high milk production. Twelve such cows were used to determine AFM1 carry-over following daily oral administration of feed containing ~86 μg AFB1 for 7 days. The mean carry-over rate at steady-state (Days 3-7) was 5.8% and 2.5% in mid-lactation and late-lactation groups, respectively. The carry-over appears to increase exponentially with milk yield and could be described by the equation: carry-over% = 0.5154 e(0.0521 × milk yield), with r(2) = 0.6224. If these data truly reflect the carry-over in the national Israeli dairy herd, the maximum level of AFB1 in feed should not exceed 1.4 μg/kg, a value 3.6 times lower than the maximum residue level currently applied in Israel.
Figures
References
-
- Binder E.M., Tan L.M., Chin L.J., Handl J., Richard J. Worldwide occurrence of mycotoxins in commodities, feeds and feed ingredients. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2007;137:265–282. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2007.06.005. - DOI
-
- Council for Agricultural Science and Technology. Mycotoxins: Economic and Health Risks. CAST; Ames, IA, USA: 1989. p. 99.
-
- Council for Agricultural Science and Technology. Mycotoxins: Risks in Plant, Animal, and Human Systems. CAST; Ames, IA, USA: 2003.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

