Tissue artifact removal from respiratory signals based on empirical mode decomposition
- PMID: 23325303
- PMCID: PMC3625471
- DOI: 10.1007/s10439-013-0742-5
Tissue artifact removal from respiratory signals based on empirical mode decomposition
Abstract
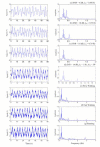
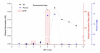
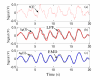
On-line measurement of respiration plays an important role in monitoring human physical activities. Such measurement commonly employs sensing belts secured around the rib cage and abdomen of the test object. Affected by the movement of body tissues, respiratory signals typically have a low signal-to-noise ratio. Removing tissue artifacts therefore is critical to ensuring effective respiration analysis. This paper presents a signal decomposition technique for tissue artifact removal from respiratory signals, based on the empirical mode decomposition (EMD). An algorithm based on the mutual information and power criteria was devised to automatically select appropriate intrinsic mode functions for tissue artifact removal and respiratory signal reconstruction. Performance of the EMD-algorithm was evaluated through simulations and real-life experiments (N = 105). Comparison with low-pass filtering that has been conventionally applied confirmed the effectiveness of the technique in tissue artifacts removal.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Empirical mode decomposition applied to tissue artifact removal from respiratory signal.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2008;2008:3624-7. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2008.4649991. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2008. PMID: 19163494
-
Application of Empirical Mode Decomposition Combined With Notch Filtering for Interpretation of Surface Electromyograms During Functional Electrical Stimulation.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2017 Aug;25(8):1268-1277. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2624763. Epub 2016 Nov 3. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2017. PMID: 27834646 Clinical Trial.
-
[The elimination of movement artifact in pulse signals].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Jun;27(3):552-5. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20649017 Chinese.
-
Methods for artifact detection and removal from scalp EEG: A review.Neurophysiol Clin. 2016 Nov;46(4-5):287-305. doi: 10.1016/j.neucli.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Neurophysiol Clin. 2016. PMID: 27751622 Review.
-
A review of data fusion techniques.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Oct 27;2013:704504. doi: 10.1155/2013/704504. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24288502 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation coefficient local capping REMD adaptive filtering method for laser interference signal.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 21;17(1):e0261875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261875. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35061729 Free PMC article.
-
New Respiratory Inductive Plethysmography (RIP) Method for Evaluating Ventilatory Adaptation during Mild Physical Activities.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 23;11(3):e0151983. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151983. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27008313 Free PMC article.
-
Telemonitoring Techniques for Lung Volume Measurement: Accuracy, Artifacts and Effort.Front Digit Health. 2020 Sep 17;2:559483. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2020.559483. eCollection 2020. Front Digit Health. 2020. PMID: 34713036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Empirical mode decomposition and neural network for the classification of electroretinographic data.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2014 Jul;52(7):619-28. doi: 10.1007/s11517-014-1164-8. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2014. PMID: 24923413
-
Instantaneous Respiratory Estimation from Thoracic Impedance by Empirical Mode Decomposition.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Jul 7;15(7):16372-87. doi: 10.3390/s150716372. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26198231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen K, Ladd W, Beams D, Sheers W, Radwin R, Tompkins W, Webster J. Comparison of impedance and inductance ventilation sensors on adults during breathing, motion, and simulated airway obstruction. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 1997;44:555–566. - PubMed
-
- Varady P, Micsik T, Benedek S, Benyo Z. A novel method for the detection of apnea and hypopnea events in respiration signals. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 2002;49:936–942. - PubMed
-
- Binks A, Banzett R, Duvivier C. An inexpensive, MRI compatible device to measure tidal volume from chest-wall circumference. Physiological Measurement. 2007;28:149–159. - PubMed
-
- Pennock B. Rib cage and abdominal piezoelectric film belts to measure ventilatory airflow. Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing. 1990;6:276–283. - PubMed
-
- Witt J, Fisher J, Guenette J, Cheong K, Wilson B, Sheel A. Measurement of exercise ventilation by a portable respiratory inductive plethysmograph. Respiratory Physiology and Neurobiology. 2006;154:389–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

