Parental oxytocin and early caregiving jointly shape children's oxytocin response and social reciprocity
- PMID: 23325323
- PMCID: PMC3656367
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2013.22
Parental oxytocin and early caregiving jointly shape children's oxytocin response and social reciprocity
Abstract
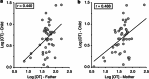
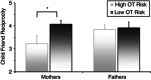
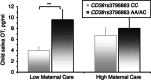
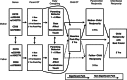
Oxytocin (OT) has an important role in bond formation and social reciprocity, and animal studies indicate that OT functioning is transferred from parent to child through patterns of parental care. Perspectives on attachment suggest that the individual's various attachment bonds are underpinned by the oxytocinergic system. However, prospective human studies that demonstrate the cross-generation transfer of OT as mediated by early caregiving and its impact on children's multiple attachments are lacking. To address these concerns, the current study included 160 mothers and fathers and their firstborn child who participated in a 3-year longitudinal study. At the first and sixth postpartum months, parents' plasma OT was assayed, parent-infant interactions were videotaped and micro-coded, and allelic variations on the OXTR(rs2254298, rs1042778) and CD38rs3796863 genes were measured. At 3 years, parents' and child's salivary OT was assessed and children's social reciprocity observed during interactions with mother, father, and their first best friend. Parents' OT levels were individually stable across the 3-year period, correlated with low-risk OXTR and CD38 alleles, and predicted child OT. Child's social reciprocity with friend was associated with child OT levels, mother's OT-related genes and hormones, and mother-child reciprocity, but not with father's genes, hormones, or behavior. A cross-generation gene-by-environment effect emerged, with low child OT levels predicted by the interaction of maternal high-risk CD38 allele and diminished maternal care in infancy. These results demonstrate individual stability in peripheral OT across several years and describe a cross-generation transfer of OT through caregiving in humans within a prospective longitudinal design. Consistent with other mammals, biobehavioral experiences within the parent-infant bond shape children's affiliative biology and social behavior across multiple attachments. Our findings bear important implications for conditions involving disruptions to maternal-infant bonding and underscore the potential for peer-based interventions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic and peripheral markers of the oxytocin system and parental care jointly support the cross-generational transmission of bonding across three generations.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019 Apr;102:172-181. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.12.004. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30572177
-
Sensitive parenting is associated with plasma oxytocin and polymorphisms in the OXTR and CD38 genes.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Aug 1;72(3):175-81. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.12.025. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22336563
-
Oxytocin administration to parent enhances infant physiological and behavioral readiness for social engagement.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Dec 15;72(12):982-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.06.011. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22795645 Clinical Trial.
-
Oxytocin Pathway Genes: Evolutionary Ancient System Impacting on Human Affiliation, Sociality, and Psychopathology.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Feb 1;79(3):174-84. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26392129 Review.
-
Oxytocin and social affiliation in humans.Horm Behav. 2012 Mar;61(3):380-91. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Horm Behav. 2012. PMID: 22285934 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurogenetic and epigenetic correlates of adolescent predisposition to and risk for addictive behaviors as a function of prefrontal cortex dysregulation.J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2015 May;25(4):286-92. doi: 10.1089/cap.2014.0146. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25919973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Childhood adversity and parenting behavior: the role of oxytocin receptor gene polymorphisms.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2019 Jun;126(6):777-787. doi: 10.1007/s00702-019-02009-9. Epub 2019 May 16. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2019. PMID: 31098723
-
Salivary Oxytocin Is Negatively Associated With Religious Faith in Japanese Non-Abrahamic People.Front Psychol. 2021 Aug 26;12:705781. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.705781. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34512461 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological Implications of Parent-Child Emotional Availability: A Review.Brain Sci. 2021 Jul 30;11(8):1016. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11081016. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34439635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perception of social synchrony induces mother-child gamma coupling in the social brain.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017 Jul 1;12(7):1036-1046. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsx032. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28402479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartz JA, Zaki J, Bolger N, Ochsner KN. Social effects of oxytocin in humans: context and person matter. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011;15:301–309. - PubMed
-
- Baumeister RF, Leary MR. The need to belong—desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human-motivation. Psychol Bull. 1995;117:497–529. - PubMed
-
- Belsky J. Early human-experience—a family perspective. Dev Psychol. 1981;17:3–23.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

