Contribution of increased VEGF receptors to hypoxic changes in fetal ovine carotid artery contractile proteins
- PMID: 23325408
- PMCID: PMC3625715
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00110.2012
Contribution of increased VEGF receptors to hypoxic changes in fetal ovine carotid artery contractile proteins
Abstract
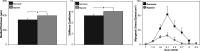
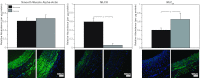
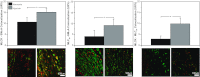
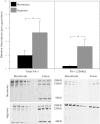
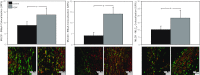
Recent studies suggest that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) can modulate smooth muscle phenotype and, consequently, the composition and function of arteries upstream from the microcirculation, where angiogenesis occurs. Given that hypoxia potently induces VEGF, the present study explores the hypothesis that, in fetal arteries, VEGF contributes to hypoxic vascular remodeling through changes in abundance, organization, and function of contractile proteins. Pregnant ewes were acclimatized at sea level or at altitude (3,820 m) for the final 110 days of gestation. Endothelium-denuded carotid arteries from full-term fetuses were used fresh or after 24 h of organ culture in a physiological concentration (3 ng/ml) of VEGF. After 110 days, hypoxia had no effect on VEGF abundance but markedly increased abundance of the Flk-1 (171%) and Flt-1 (786%) VEGF receptors. Hypoxia had no effect on smooth muscle α-actin (SMαA), decreased myosin light chain (MLC) kinase (MLCK), and increased 20-kDa regulatory MLC (MLC(20)) abundances. Hypoxia also increased MLCK-SMαA, MLC(20)-SMαA, and MLCK-MLC(20) colocalization. Compared with hypoxia, organ culture with VEGF produced the same pattern of changes in contractile protein abundance and colocalization. Effects of VEGF on colocalization were blocked by the VEGF receptor antagonists vatalanib (240 nM) and dasatinib (6.3 nM). Thus, through increases in VEGF receptor density, hypoxia can recruit VEGF to help mediate remodeling of fetal arteries upstream from the microcirculation. The results support the hypothesis that VEGF contributes to hypoxic vascular remodeling through changes in abundance, organization, and function of contractile proteins.
Figures




References
-
- Agnati LF, Fuxe K, Torvinen M, Genedani S, Franco R, Watson S, Nussdorfer GG, Leo G, Guidolin D. New methods to evaluate colocalization of fluorophores in immunocytochemical preparations as exemplified by a study on A2A and D2 receptors in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Histochem Cytochem 53: 941–953, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bagwell CB, Hudson JL, Irvin GL., 3rd Nonparametric flow cytometry analysis. J Histochem Cytochem 27: 293–296, 1979 - PubMed
-
- Belik J, Kerc E, Pato MD. Rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase and phosphatase activities decrease with age. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290: L509–L516, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

