Transplantation for acute liver failure in patients exposed to NSAIDs or paracetamol (acetaminophen): the multinational case-population SALT study
- PMID: 23325533
- PMCID: PMC3568201
- DOI: 10.1007/s40264-012-0013-7
Transplantation for acute liver failure in patients exposed to NSAIDs or paracetamol (acetaminophen): the multinational case-population SALT study
Abstract
Background: Most NSAIDs are thought to be able to cause hepatic injury and acute liver failure (ALF), but the event rates of those leading to transplantation (ALFT) remain uncertain.
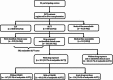
Objectives: The aim of the study was to estimate population event rates for NSAID-associated ALFT METHODS: This was a case-population study of ALFT in 57 eligible liver transplant centres in seven countries (France, Greece, Ireland, Italy, The Netherlands, Portugal and the UK). Cases were all adults registered from 2005 to 2007 for a liver transplant following ALFT without identified clinical aetiology, exposed to an NSAID or paracetamol (acetaminophen) within 30 days before the onset of clinical symptoms. NSAID and paracetamol population exposures were assessed using national sales data from Intercontinental Marketing Services (IMS). Risk was estimated as the rate of ALFT per million treatment-years (MTY).
Results: In the 52 participating centres, 9479 patients were registered for transplantation, with 600 for ALFT, 301 of whom, without clinical aetiology, had been exposed to a drug within 30 days. Of these 301 patients, 40 had been exposed to an NSAID and 192 to paracetamol (81 of whom were without overdose). Event rates per MTY were 1.59 (95 % CI 1.1-2.2) for all NSAIDs pooled, 2.3 (95 % CI 1.2-3.9) for ibuprofen, 1.9 (95 % CI 0.8-3.7) for nimesulide, 1.6 (95 % CI 0.6-3.4) for diclofenac and 1.6 (95 % CI 0.3-4.5) for ketoprofen. For paracetamol, the event rate was 3.3 per MTY (95 % CI 2.6-4.1) without overdoses and 7.8 (95 % CI 6.8-9.0) including overdoses.
Conclusions: ALF leading to registration for transplantation after exposure to an NSAID was rare, with no major difference between NSAID. Non-overdose paracetamol-exposed liver failure was twice more common than NSAID-exposed liver failure.
Figures

References
-
- Danan G, Trunet P, Bernuau J, Degott C, Babany G, Pessayre D, et al. Pirprofen-induced fulminant hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1985;89(1):210–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

