Is the TAM receptor Axl a receptor for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus?
- PMID: 23325690
- PMCID: PMC3624193
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.03268-12
Is the TAM receptor Axl a receptor for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus?
Abstract
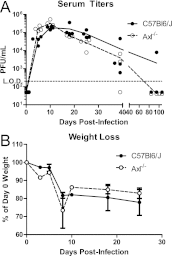
A recent publication indicated that overexpression of Axl, a cellular receptor that negatively regulates Toll-like receptor signaling, enhanced the entry of viruses pseudotyped with the glycoprotein of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) in vitro. In testing the biological relevance of these observations, we found differences in neither viral kinetics between LCMV infections of Axl(-/-) and wild-type mice nor T-cell responses prior to spontaneous viral clearance. Thus, Axl is not required for productive LCMV infection of mice.
Figures
References
-
- Scott RS, McMahon EJ, Pop SM, Reap EA, Caricchio R, Cohen PL, Earp HS, Matsushima GK. 2001. Phagocytosis and clearance of apoptotic cells is mediated by MER. Nature 411:207–211 - PubMed
-
- Behrens EM, Gadue P, Gong SY, Garrett S, Stein PL, Cohen PL. 2003. The mer receptor tyrosine kinase: expression and function suggest a role in innate immunity. Eur. J. Immunol. 33:2160–2167 - PubMed
-
- Rothlin CV, Ghosh S, Zuniga EI, Oldstone MB, Lemke G. 2007. TAM receptors are pleiotropic inhibitors of the innate immune response. Cell 131:1124–1136 - PubMed
-
- Brown JE, Krodel M, Pazos M, Lai C, Prieto AL. 2012. Cross-phosphorylation, signaling and proliferative functions of the Tyro3 and Axl receptors in Rat2 cells. PLoS One 7:e36800 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036800 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

