Spatial stochastic modelling of the Hes1 gene regulatory network: intrinsic noise can explain heterogeneity in embryonic stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 23325756
- PMCID: PMC3565746
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0988
Spatial stochastic modelling of the Hes1 gene regulatory network: intrinsic noise can explain heterogeneity in embryonic stem cell differentiation
Abstract
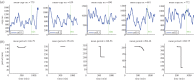
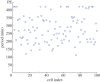
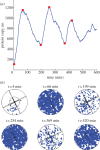
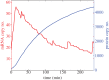
Individual mouse embryonic stem cells have been found to exhibit highly variable differentiation responses under the same environmental conditions. The noisy cyclic expression of Hes1 and its downstream genes are known to be responsible for this, but the mechanism underlying this variability in expression is not well understood. In this paper, we show that the observed experimental data and diverse differentiation responses can be explained by a spatial stochastic model of the Hes1 gene regulatory network. We also propose experiments to control the precise differentiation response using drug treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The cyclic gene Hes1 contributes to diverse differentiation responses of embryonic stem cells.Genes Dev. 2009 Aug 15;23(16):1870-5. doi: 10.1101/gad.1823109. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19684110 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative genomic analyses on HES/HEY family: Notch-independent HES1, HES3 transcription in undifferentiated ES cells, and Notch-dependent HES1, HES5, HEY1, HEY2, HEYL transcription in fetal tissues, adult tissues, or cancer.Int J Oncol. 2007 Aug;31(2):461-6. Int J Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17611704
-
Expression dynamics and functions of Hes factors in development and diseases.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;110:263-83. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-405943-6.00007-5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25248479 Review.
-
Hes1 regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation by suppressing Notch signaling.Genes Cells. 2010 Jun;15(7):689-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2010.01413.x. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Genes Cells. 2010. PMID: 20545770 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and mechanism of ultradian oscillatory expression of the mouse Hes genes.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Oct;34:85-90. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.04.038. Epub 2014 May 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24865153 Review.
Cited by
-
Is the Cell Nucleus a Necessary Component in Precise Temporal Patterning?PLoS One. 2015 Jul 30;10(7):e0134239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134239. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26226505 Free PMC article.
-
The Linear Noise Approximation for Spatially Dependent Biochemical Networks.Bull Math Biol. 2019 Aug;81(8):2873-2901. doi: 10.1007/s11538-018-0428-0. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Bull Math Biol. 2019. PMID: 29644520 Free PMC article.
-
The role of dimerisation and nuclear transport in the Hes1 gene regulatory network.Bull Math Biol. 2014 Apr;76(4):766-98. doi: 10.1007/s11538-013-9842-5. Epub 2013 May 18. Bull Math Biol. 2014. PMID: 23686434 Free PMC article.
-
Smart computational exploration of stochastic gene regulatory network models using human-in-the-loop semi-supervised learning.Bioinformatics. 2019 Dec 15;35(24):5199-5206. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz420. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31141124 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic comparison of modeling fidelity levels and parameter inference settings applied to negative feedback gene regulation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Dec 15;18(12):e1010683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010683. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36520957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirata H, Yoshiura S, Ohtsuka T, Bessho Y, Harada T, Yoshikawa K, Kageyama R. 2002. Oscillatory expression of the bHLH factor Hes1 regulated by a negative feedback loop. Science 298, 840–84310.1126/science.1074560 (doi:10.1126/science.1074560) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geva-Zatorsky N, et al. 2006. Oscillations and variability in the p53 system. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2, E1–E1310.1038/msb4100068 (doi:10.1038/msb4100068) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nelson DE, et al. 2004. Oscillations in NF-kB signaling control the dynamics of gene expression. Science 306, 704–70810.1126/science.1099962 (doi:10.1126/science.1099962) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shankaran H, Ippolito DL, Chrisler WB, Resat H, Bollinger N, Opresko LK, Wiley HS. 2009. Rapid and sustained nuclear-cytoplasmic ERK oscillations induced by epidermal growth factor. Mol. Syst. Biol. 5, 332.10.1038/msb.2009.90 (doi:10.1038/msb.2009.90) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sang L, Coller HA, Roberts JM. 2008. Control of the reversibility of cellular quiescence by the transcriptional repressor HES1. Science 321, 1095–110010.1126/science.1155998 (doi:10.1126/science.1155998) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

