The microRNA miR-7 regulates Tramtrack69 in a developmental switch in Drosophila follicle cells
- PMID: 23325762
- PMCID: PMC3557780
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.080192
The microRNA miR-7 regulates Tramtrack69 in a developmental switch in Drosophila follicle cells
Abstract
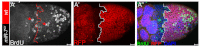
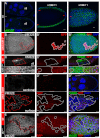
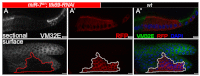
Development in multicellular organisms includes both small incremental changes and major switches of cell differentiation and proliferation status. During Drosophila oogenesis, the follicular epithelial cells undergo two major developmental switches that cause global changes in the cell-cycle program. One, the switch from the endoreplication cycle to a gene-amplification phase, during which special genomic regions undergo repeated site-specific replication, is attributed to Notch downregulation, ecdysone signaling activation and upregulation of the zinc-finger protein Tramtrack69 (Ttk69). Here, we report that the microRNA miR-7 exerts an additional layer of regulation in this developmental switch by regulating Ttk69 transcripts. miR-7 recognizes the 3' UTR of ttk69 transcripts and regulates Ttk69 expression in a dose-dependent manner. Overexpression of miR-7 effectively blocks the switch from the endocycle to gene amplification through its regulation of ttk69. miR-7 and Ttk69 also coordinate other cell differentiation events, such as vitelline membrane protein expression, that lead to the formation of the mature egg. Our studies reveal the important role miR-7 plays in developmental decision-making in association with signal-transduction pathways.
Figures
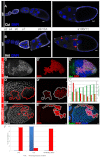
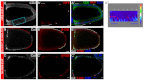
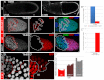
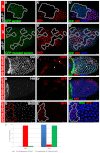
References
-
- Assa-Kunik E., Torres I. L., Schejter E. D., Johnston D. S., Shilo B. Z. (2007). Drosophila follicle cells are patterned by multiple levels of Notch signaling and antagonism between the Notch and JAK/STAT pathways. Development 134, 1161-1169 - PubMed
-
- Berezikov E., Robine N., Samsonova A., Westholm J. O., Naqvi A., Hung J. H., Okamura K., Dai Q., Bortolamiol-Becet D., Martin R., et al. (2011). Deep annotation of Drosophila melanogaster microRNAs yields insights into their processing, modification, and emergence. Genome Res. 21, 203-215 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernardi F., Romani P., Tzertzinis G., Gargiulo G., Cavaliere V. (2009). EcR-B1 and Usp nuclear hormone receptors regulate expression of the VM32E eggshell gene during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 328, 541-551 - PubMed
-
- Betel D., Wilson M., Gabow A., Marks D. S., Sander C. (2008). The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D149-D153 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

