cAMP-stimulated phosphorylation of diaphanous 1 regulates protein stability and interaction with binding partners in adrenocortical cells
- PMID: 23325789
- PMCID: PMC3596254
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-08-0597
cAMP-stimulated phosphorylation of diaphanous 1 regulates protein stability and interaction with binding partners in adrenocortical cells
Abstract
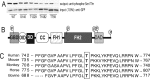
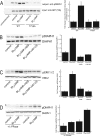
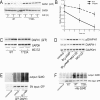
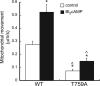
Diaphanous homologue 1 (DIAPH1) is a Rho effector protein that coordinates cellular dynamics by regulating microfilament and microtubule function. We previously showed that DIAPH1 plays an integral role in regulating the production of cortisol by controlling the rate of mitochondrial movement, by which activation of the adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)/cAMP signaling pathway stimulates mitochondrial trafficking and promotes the interaction between RhoA and DIAPH1. In the present study we use mass spectrometry to identify DIAPH1 binding partners and find that DIAPH1 interacts with several proteins, including RhoA, dynamin-1, kinesin, β-tubulin, β-actin, oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP)-related protein 2 (ORP2), and ORP10. Moreover, DIAPH1 is phosphorylated in response to dibutyryl cAMP (Bt2cAMP) at Thr-759 via a pathway that requires extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK). Alanine substitution of Thr-759 renders DIAPH1 more stable and attenuates the interaction between DIAPH1 and kinesin, ORP2, and actin but has no effect on the ability of the protein to interact with RhoA or β-tubulin. Finally, overexpression of a DIAPH1 T759A mutant significantly decreases the rate of Bt2cAMP-stimulated mitochondrial movement. Taken together, our findings establish a key role for phosphorylation in regulating the stability and function of DIAPH1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RhoA and DIAPH1 mediate adrenocorticotropin-stimulated cortisol biosynthesis by regulating mitochondrial trafficking.Endocrinology. 2010 Sep;151(9):4313-23. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0044. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20591975 Free PMC article.
-
Negative cooperativity regulates ligand activation of DIAPH1 and other diaphanous related formins.Commun Biol. 2025 May 21;8(1):776. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08222-5. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40399622 Free PMC article.
-
The scaffold-protein IQGAP1 enhances and spatially restricts the actin-nucleating activity of Diaphanous-related formin 1 (DIAPH1).J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):3134-3147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010476. Epub 2020 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32005666 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of adrenocortical steroid hormone production by RhoA-diaphanous 1 signaling and the cytoskeleton.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 May 22;371(1-2):79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.11.014. Epub 2012 Nov 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23186810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OSBP-related protein 2 (ORP2): Unraveling its functions in cellular lipid/carbohydrate metabolism, signaling and F-actin regulation.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Sep;192:105298. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.01.016. Epub 2019 Feb 2. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30716465 Review.
Cited by
-
OSBPL2 encodes a protein of inner and outer hair cell stereocilia and is mutated in autosomal dominant hearing loss (DFNA67).Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015 Feb 10;10:15. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0238-5. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015. PMID: 25759012 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-actin cytoskeleton crosstalk in cell migration.J Cell Physiol. 2022 May;237(5):2387-2403. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30729. Epub 2022 Mar 27. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35342955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formin' cellular structures: Physiological roles of Diaphanous (Dia) in actin dynamics.Commun Integr Biol. 2013 Nov 1;6(6):e27634. doi: 10.4161/cib.27634. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Commun Integr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24719676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yersinia effector YopO uses actin as bait to phosphorylate proteins that regulate actin polymerization.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Mar;22(3):248-55. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2964. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25664724 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Mlkl or Ripk3 deletion on age-associated liver inflammation, metabolic health, and lifespan.Geroscience. 2025 Jun;47(3):4465-4483. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01553-5. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39930289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberts AS. Identification of a carboxyl-terminal diaphanous-related formin homology protein autoregulatory domain. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:2824–2830. - PubMed
-
- Alberts AS, Bouquin N, Johnston LH, Treisman R. Analysis of RhoA-binding proteins reveals an interaction domain conserved in heterotrimeric G protein beta subunits and the yeast response regulator protein Skn7. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:8616–8622. - PubMed
-
- Allan VJ, Schroer TA. Membrane motors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:476–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

