Heparin rescues factor V Leiden-associated placental failure independent of anticoagulation in a murine high-risk pregnancy model
- PMID: 23325830
- PMCID: PMC3952382
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-08-448209
Heparin rescues factor V Leiden-associated placental failure independent of anticoagulation in a murine high-risk pregnancy model
Abstract
Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is being tested as an experimental drug for improving pregnancy outcome in women with inherited thrombophilia and placenta-mediated pregnancy complications, such as recurrent pregnancy loss. The role of thrombotic processes in these disorders remains unproven, and the issue of antithrombotic prophylaxis is intensely debated. Using a murine model of factor V Leiden-associated placental failure, we show that treatment of the mother with LMWH allows placental development to proceed and affords significant protection from fetal loss. Nonetheless, the therapeutic effect of LMWH is not replicated by anticoagulation; fondaparinux and a direct Xa inhibitor, C921-78, achieve anticoagulation similar to LMWH but produce little or no improvement in pregnancy outcome. Genetic attenuation of maternal platelet aggregation is similarly ineffective. In contrast, even a partial loss of thrombin sensitivity of maternal platelets protects pregnancies. Neonates born from these pregnancies are growth retarded, suggesting that placental function is only partially restored. The placentae are smaller but do not reveal any evidence of thrombosis. Our data demonstrate an anticoagulation-independent role of LMWH in protecting pregnancies and provide evidence against the involvement of thrombotic processes in thrombophilia-associated placental failure. Importantly, thrombin-mediated maternal platelet activation remains central in the mechanism of placental failure.
Figures
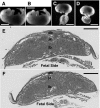
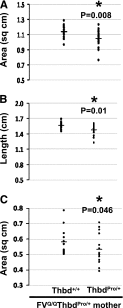
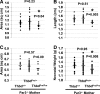
Comment in
-
Heparin--not only thinning the blood.Blood. 2013 Mar 14;121(11):1932-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-480475. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23493771
Similar articles
-
Heparin--not only thinning the blood.Blood. 2013 Mar 14;121(11):1932-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-480475. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23493771
-
Is heparin a placental anticoagulant in high-risk pregnancies?Blood. 2011 Nov 3;118(18):4780-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-319749. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21868576 Review.
-
Ultrasound diagnosis of severe thrombotic placental damage in the second trimester: an observational study.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2004 May;23(5):472-6. doi: 10.1002/uog.1044. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2004. PMID: 15133798
-
[Thrombophilia, preeclampsia and other pregnancy complications].Acta Med Croatica. 2009 Oct;63(4):297-305. Acta Med Croatica. 2009. PMID: 20034330 Review. Croatian.
-
LMWH to prevent placenta-mediated pregnancy complications: an update.Br J Haematol. 2015 Mar;168(5):619-38. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13209. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25399526 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-molecular-weight heparin for the prevention of preeclampsia in high-risk pregnancies without thrombophilia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Jan 17;24(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06218-9. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38233773 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombophilia and Pregnancy Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 30;16(12):28418-28. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226104. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26633369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of inherited thrombophilia in pregnancy.Womens Health (Lond). 2016 Jul;12(4):433-41. doi: 10.1177/1745505716653702. Womens Health (Lond). 2016. PMID: 27638899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maintaining extraembryonic expression allows generation of mice with severe tissue factor pathway inhibitor deficiency.Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 12;3(3):489-498. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018018853. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 30755437 Free PMC article.
-
Enoxaparin for prevention of unexplained recurrent miscarriage: a multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial.Blood. 2015 Apr 2;125(14):2200-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-11-610857. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25636341 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Barker DJ, Osmond C, Kajantie E, et al. Growth and chronic disease: findings in the Helsinki Birth Cohort. Ann Hum Biol. 2009;36(5):445–458. - PubMed
-
- Benedetto C, Marozio L, Tavella AM, et al. Coagulation disorders in pregnancy: acquired and inherited thrombophilias. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1205:106–117. - PubMed
-
- Robertson L, Wu O, Langhorne P, et al. Thrombosis: Risk and Economic Assessment of Thrombophilia Screening (TREATS) Study. Thrombophilia in pregnancy: a systematic review. Br J Haematol. 2006;132(2):171–196. - PubMed
-
- Brenner B, Hoffman R, Carp H, et al. LIVE-ENOX Investigators. Efficacy and safety of two doses of enoxaparin in women with thrombophilia and recurrent pregnancy loss: the LIVE-ENOX study. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(2):227–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

