NK cell responses to cytomegalovirus infection lead to stable imprints in the human KIR repertoire and involve activating KIRs
- PMID: 23325834
- PMCID: PMC3617633
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-10-459545
NK cell responses to cytomegalovirus infection lead to stable imprints in the human KIR repertoire and involve activating KIRs
Abstract
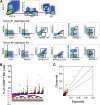
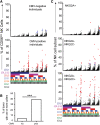
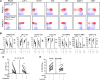
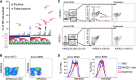
Human natural killer (NK) cells are functionally regulated by killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) and their interactions with HLA class I molecules. As KIR expression in a given NK cell is genetically hard-wired, we hypothesized that KIR repertoire perturbations reflect expansions of unique NK-cell subsets and may be used to trace adaptation of the NK-cell compartment to virus infections. By determining the human "KIR-ome" at a single-cell level in more than 200 donors, we were able to analyze the magnitude of NK cell adaptation to virus infections in healthy individuals. Strikingly, infection with human cytomegalovirus (CMV), but not with other common herpesviruses, induced expansion and differentiation of KIR-expressing NK cells, visible as stable imprints in the repertoire. Education by inhibitory KIRs promoted the clonal-like expansion of NK cells, causing a bias for self-specific inhibitory KIRs. Furthermore, our data revealed a unique contribution of activating KIRs (KIR2DS4, KIR2DS2, or KIR3DS1), in addition to NKG2C, in the expansion of human NK cells. These results provide new insight into the diversity of KIR repertoire and its adaptation to virus infection, suggesting a role for both activating and inhibitory KIRs in immunity to CMV infection.
Figures



References
-
- Barrow AD, Trowsdale J. The extended human leukocyte receptor complex: diverse ways of modulating immune responses. Immunol Rev. 2008;224:98–123. - PubMed
-
- Braud VM, Allan DS, O’Callaghan CA, et al. HLA-E binds to natural killer cell receptors CD94/NKG2A, B and C. Nature. 1998;391(6669):795–799. - PubMed
-
- Moretta L, Moretta A. Killer immunoglobulin-like receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16(5):626–633. - PubMed
-
- Parham P. MHC class I molecules and KIRs in human history, health and survival. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(3):201–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

