Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of cefpodoxime and ciprofloxacin in acute exacerbation of chronic suppurative otitis media: A randomized, open-labeled, phase IV clinical trial
- PMID: 23326103
- PMCID: PMC3543552
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-500X.103689
Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of cefpodoxime and ciprofloxacin in acute exacerbation of chronic suppurative otitis media: A randomized, open-labeled, phase IV clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness and safety of cefpodoxime and ciprofloxacin for the treatment of mild to moderate cases of acute exacerbation of chronic suppurative otitis media (AECSOM).
Materials and methods: Adult patients diagnosed with AECSOM were screened and patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria were randomized to receive either cefpodoxime 200 mg twice daily or ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily orally for 7 days. The primary outcome of this randomized, open-labeled, phase IV clinical trial (Registration Number - CTRI/2011/10/002079) was clinical success rate at day 14 visit and the secondary outcome was incidence of adverse events (AEs). Forty-six patients were enrolled: 23 in the cefpodoxime group and 23 in the ciprofloxacin group.
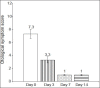
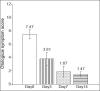
Results: The clinical success rates were 95.6% in the cefpodoxime group versus 90.9% in the ciprofloxacin group. These rates are comparable, but no statistically significant difference was observed between the groups. Few mild and self-limiting AEs were observed and the tolerability of both the drugs was also good.
Conclusion: The results of this randomized, open-labeled phase IV clinical trial showed that a 7-day course of cefpodoxime is therapeutically comparable to ciprofloxacin in terms of both clinical effectiveness and safety for the treatment of patients with AECSOM.
Keywords: CSOM; Cefpodoxime; ciprofloxacin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Verhoeff M, van der Veen EL, Rovers MM, Sanders EAM, Anne GM, Schilder AGM. Chronic suppurative otitis media: A review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;70:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Brobby GW, Zadik P. Bacteriology of otitis media in Ghana. Trop Doct. 1987;17:91–2. - PubMed
-
- Fairbanks DN. Antimicrobial therapy for chronic suppurative otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1981;90:S58–62. - PubMed
-
- Chronic suppurative otitis media-Burden of Illness and Management Options. [monograph on the internet] World health organization. 2004. [Last accessed on 2011 Nov 15]. Available from: http://www.who.int/entity/pbd/deafness/activities/hearing…/otitis_media.pdf .
-
- Bluestone CD, Kenna MA. Chronic suppurative otitits media: Antimicrobial therapy or surgery? Pediatr Ann. 1984;13:417–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources